There are several different Diaphragmatic hernia symptoms you may experience. These symptoms include a difficulty swallowing and the stomach’s contents flowing back into the oesophagus. In addition, you may experience increased heart pressure after eating and circulatory problems. If you experience any of these symptoms, you may need to see a doctor for evaluation.
Diaphragmatic hernia
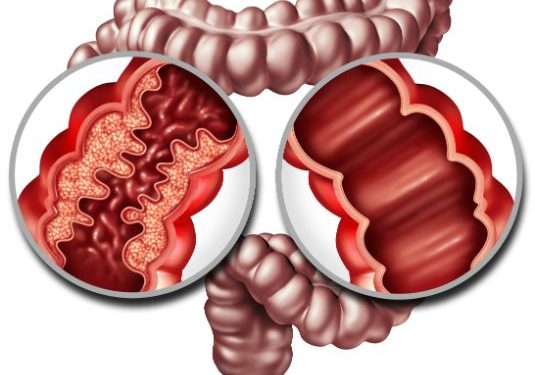
Diaphragmatic hernia is a type of hernia caused by a weakening of the diaphragm, a sheet-like muscle that separates the abdominal cavity from the chest. When a hernia ruptures, the abdominal contents can slide backward into the chest area, creating an emergency situation that requires surgery.
Diaphragmatic hernia can be painful and cause difficulty swallowing. It can also contribute to GERD and heartburn. Diaphragmatic hernia is often treatable with minimally-invasive surgery. Dr. Mark Reiner is an expert in this field, having performed thousands of advanced laparoscopic hiatal hernia surgeries.
Diaphragmatic hernia symptoms can vary depending on the type of hernia and the location of the hernia. Type I diaphragmatic hernia symptoms include heartburn and pain in the upper abdomen. This is often the result of reflux disease, which causes the contents of the stomach to leak back into the esophagus. The stomach and esophagus’ muscles are constantly tense in an attempt to prevent acid from reaching the esophagus.
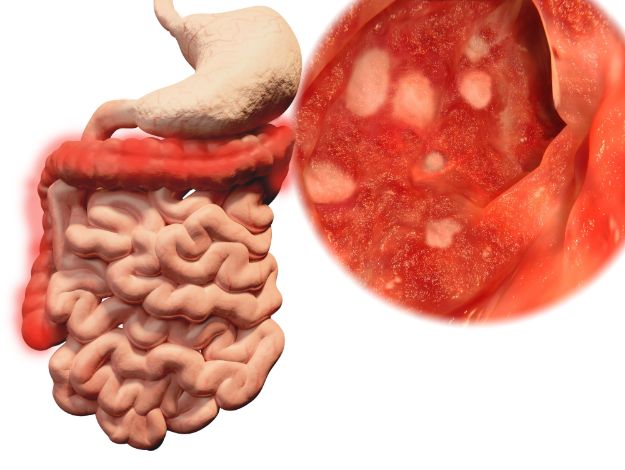
Diaphragmatic hernia symptoms can occur before or after birth. In some cases, a baby may require ECMO (extracorporeal membrane oxygenation), a machine that takes over the role of the baby’s heart and lungs. This machine helps the baby breathe by pumping blood into the body.
Diaphragmatic hernia symptoms can range from mild to severe. If you’re worried about these symptoms, it’s important to consult a doctor as soon as possible. Diaphragmatic hernia can be treated and can lead to a full recovery.
Diaphragmatic hernia can also occur during pregnancy, when a foetus forms inside the mother’s uterus. It causes organs in the abdomen to move into the chest cavity. Types of diaphragmatic hernia include the Bochdalek hernia (left-sided hernia) and the Morgagni hernia (center-side hernia).
Diaphragmatic hernias can be caused by traumatic injury to the abdomen or by congenital disorders. The most common cause of this type of hernia is trauma. If the problem is severe enough, surgery can be performed to repair the hernia. However, the success rate will depend on the strength of the child’s lungs.
Diaphragmatic hernia symptoms include pain in the chest and abdomen. A doctor will use X-rays and CT scans to diagnose the condition. A contrast study of the upper gastrointestinal tract may also be necessary for diagnosis. Diaphragmatic hernia is a serious health problem that requires immediate medical attention.
Diaphragmatic hernia symptoms in dogs include regurgitation of food and water. Some dogs also vomit greenish-yellow mucus. These symptoms usually occur within two to three months of onset. Those with the condition will need surgical repair to prevent complications.
Diaphragmatic hernia symptoms are similar to those of hiatal hernia. Symptoms can include abdominal pain, heartburn, dysphagia, and regurgitation. Some Veterans may experience only mild symptoms.

Diaphragmatic hernia symptoms in pregnancy are not always obvious. The only way to know for sure is to visit your doctor. A screening test can help determine whether your baby is developing a hernia. Diaphragmatic hernia is a common condition, and your doctor can help you get the right treatment before the birth of your baby. During your prenatal checkup, your doctor will also look at your amniotic fluid level to ensure that the fetus is developing normally.
Diaphragmatic hernia is a birth defect in which the diaphragm does not close properly. This causes the organs in the abdomen to push through and into the chest. This can affect the baby’s health, especially during the first few months of life. It can cause breathing difficulties, high blood pressure in the lungs, and other problems.
Diaphragmatic hernia is an abnormality of the diaphragm, a dome-shaped muscle that separates the lungs and heart from the abdominal organs. When it is damaged, the organs in the chest can protrude and cause problems with oxygenation, blood circulation, and digestion.
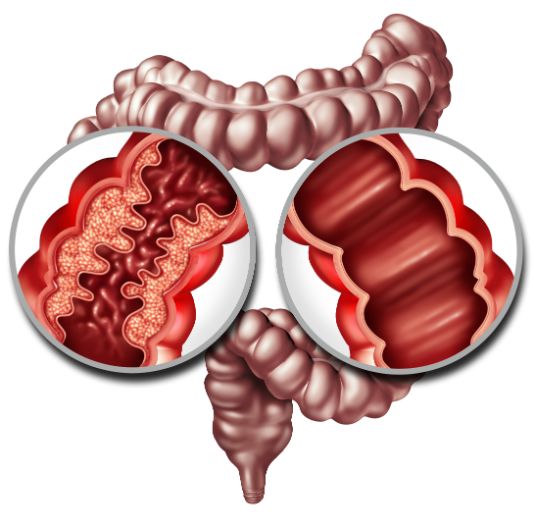
Diaphragmatic hernia in pregnancy is an uncommon but potentially life-threatening condition. The condition is generally considered a congenital defect and may require surgical repair. In cases where a hernia is diagnosed during pregnancy, conservative management is recommended to allow for fetal maturation. In one case, an emergency caesarean section was performed because the baby was not receiving adequate nutrition. However, the patient recovered well and the baby was delivered safely.
Diaphragmatic hernia surgery is a surgical procedure performed to repair the hernia and prevent further herniation of abdominal viscera. Women with symptoms should visit their doctor immediately to prevent any complications. Attempting to avoid this surgery may result in maternal and fetal mortality.

Diaphragmatic hernia is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention. Babies born with diaphragmatic hernia often cannot breathe on their own and require mechanical ventilation to survive. In extreme cases, they may even require a temporary heart/lung bypass machine. ECMO, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, is often used while a baby recovers.
A diaphragmatic hernia is a condition in which abdominal organs push up and into the chest. This can cause pulmonary hypoplasia, which is a condition in which a portion of the lungs does not fully develop. As a result, the lungs are not developed enough to support the baby’s growth.
Diaphragmatic hernia symptoms in pregnancy can be a warning sign that something is amiss. Pregnant women with diaphragmatic hernia should be monitored closely during their pregnancy to minimize the risk of complications. Vaginal delivery is discouraged because of the increased intra-abdominal pressure.
Diaphragmatic hernia is not usually visible in the first trimester, but early diagnosis greatly reduces the risk of complications. A chest x-ray is the easiest test to diagnose this condition, but more advanced tests are available at most hospitals.
Treatment options for diaphragmatic hernia
Diaphragmatic hernia is a condition where the diaphragm muscle has a hole in it and can cause the chest to swell. The resulting pressure can cause heartburn, vomiting, and breathing problems. For children, it can lead to significant lung problems and growth problems. Some babies may have to use special feeding tubes to get adequate nutrition. The condition can also lead to developmental delays, including the inability to roll over, crawl, and stand. The lungs need time to develop and grow normally.
If the hernia is severe, a doctor may suggest surgery. However, this is often not an option for patients who do not suffer from severe symptoms. A change in diet and lifestyle can also help with symptoms. Avoiding spicy food, alcohol, and high-stress levels may help relieve symptoms. Additionally, obesity is a risk factor for diaphragmatic hernia, so losing weight can help.
Although diaphragmatic hernia is rare, it can be life-threatening. Traumatic or congenital conditions can cause the diaphragm to rip. A diaphragmatic hernia occurs in approximately 5% of closed thoracoabdominal injuries. Symptoms may range from a lack of symptoms to severe chest pain. Diagnosis is usually based on clinical signs and anamnesis, but often requires imaging to confirm a diagnosis.
The diaphragm is a thin layer of muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity. It is a major muscle and plays a key role in breathing. When the diaphragm is damaged, it will cause an obstruction that prevents the growth of the lungs. This may lead to pulmonary hypoplasia, a condition where one or both lungs are not developed properly.
Diaphragmatic hernia is an emergency situation that requires prompt medical attention and treatment. The condition develops in the womb when a baby’s diaphragm is not fully developed, allowing organs from the abdomen to spill into the chest cavity. Because of this, immediate surgical attention is required.
CDH can also lead to long-term health complications for children. In some cases, these problems can be more serious than those associated with other congenital abnormalities. Some patients may require long-term oxygenation and respiratory support. Depending on the severity of the condition, some children may even require ECMO support. These problems require multidisciplinary care to prevent complications and promote the child’s recovery.
Diaphragmatic hernia is rare in adults. Most cases occur during childhood. It is caused by a failure of the diaphragm muscle during prenatal development. The abdominal organs become trapped in the chest cavity, and the lungs cannot fully develop.