Symptoms of hypertrophic osteoarthropathy can vary. The disease can be classified into primary and secondary forms, depending on the cause of the disease. The most common secondary form of hypertrophic osteoarthropathy is associated with lung cancer. Other neoplasms, such as lymphoma and melanoma, can also cause secondary hypertrophic osteoarthropathy.
In some cases, the underlying cause of hypertrophic osteoarthropathy may be an infection. In this case, the infection can be treated using antibiotics or antimicrobial therapy. The patient can also undergo surgery. The surgery may include removal of the prosthetic vascular graft. This procedure may be accompanied by systemic antibiotic therapy to prevent an infection from spreading.
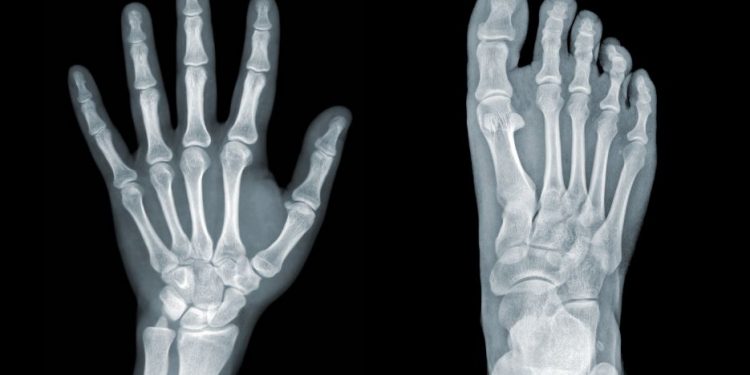
The diagnosis of hypertrophic osteoarthropathy requires clinical examination and a bone scan. A technetium bone scan can show the presence of thickening of the bones. This thickening can be seen along the cortex and can be present in non-muscular locations. The thickening can cause tenderness or a burning sensation in the affected area. X-rays can also be used to diagnose the disease. X-rays of the wrist, femur, and tibia may show the periosteal elevation associated with hypertrophic osteoarthropathy. In most cases, the treatment is simply symptom control. Treatments can include anti-inflammatory medication, corticosteroids, bisphosphonates, and octreotide.
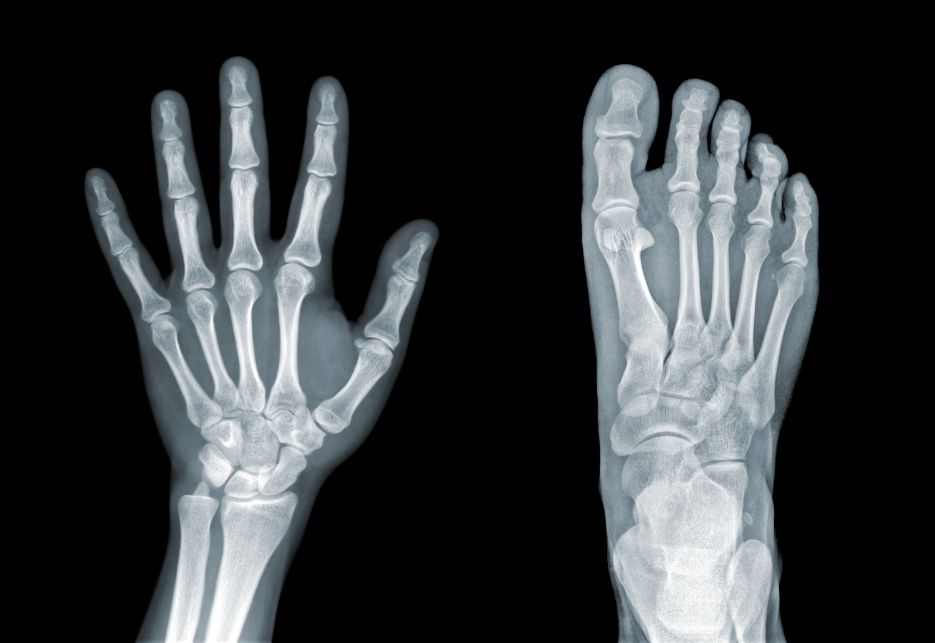
Patients with HPOA may also experience symptoms such as swelling and excruciating deep joint pain. These symptoms may be present in both children and adults. In children, the disease may be present at an earlier age than adults. The symptoms may also include a clubbing deformity of the fingers. The clubbing deformity can be caused by the growth of subungual connective tissue. The growth can cause the nails to grow out or develop drumstick appearances on the nail beds. The deformity may also be caused by a lack of oxygen in the blood.
If the disease is caused by lung cancer, it is called hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy. This condition can also affect other organs, such as the heart, liver, and kidneys. In the lungs, cancer may occur in the form of adenocarcinoma or pleural mesothelioma. The tumor can be removed by surgery, and patients can also undergo radiation therapy and antimicrobial therapy. Symptoms may subside after the tumor is removed.
The symptoms of HPOA can vary, but the most common symptoms are pain, swelling, and excruciating deep joint pain. People with HPOA may also have a burning sensation in their hands and feet, as well as painful joint effusions. This is unlike inflammatory arthritis, in which the affected area will appear red and swollen. If you notice pain in your hands and feet, see a doctor immediately. You can also take NSAIDs and other medications to help control the pain.
Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy can be caused by a variety of conditions, including cancer, infections, and genetics. However, the most common causes are lung cancer and infections. In addition, hypertrophic osteoarthropathy may be associated with other conditions, such as cancer of the appendix or other organs. Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy may remit completely with symptomatic treatment or may be a symptom of another condition, such as lupus.