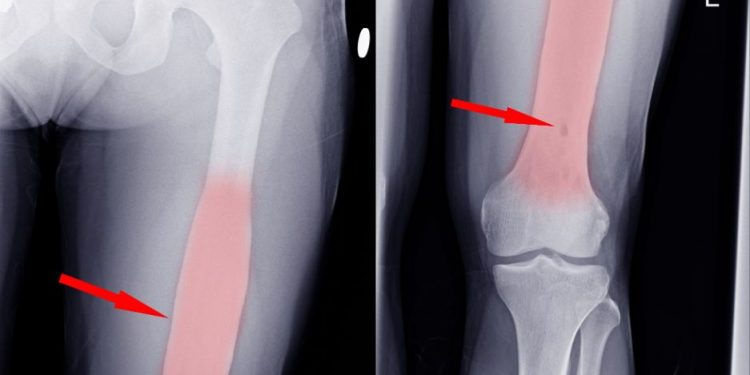
Among the most common osteosarcoma symptoms are swelling, pain, and bone fracture. The symptoms of osteosarcoma may be similar to those of other health problems, so it is important to talk to a healthcare provider to determine what symptoms you may have. You may also have other tests or imaging tests, such as a bone scan, to determine if you have osteosarcoma.
The symptoms of osteosarcoma may start as a pain in the bone, or it may appear as a lump or swelling. You may also experience a limp or pain when you walk or lift something. This pain may worsen during activity or at night. If you have any pain in the bones, you should see your doctor immediately.
A CT or MRI scan may be used to determine if you have osteosarcoma. These tests can also show if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. You may be given special dye to make the area more visible on the scan. During the procedure, the area is numbed with local anesthesia. A needle is used to remove a portion of the tumor. Your doctor may also use an open biopsy, where the tumor is removed while you are asleep.
Chemotherapy is often used before or after surgery, to destroy cancer cells. It can also shrink the tumor so that it can be more easily removed. If the tumor is too big for surgery, radiation therapy may be used. Chemotherapy helps to kill cancer cells that have spread to other parts of the body. It can also prevent the cancer from returning. Chemotherapy helps reduce pain, but it can also cause side effects such as vomiting and hair loss. It can also affect your kidney and liver.
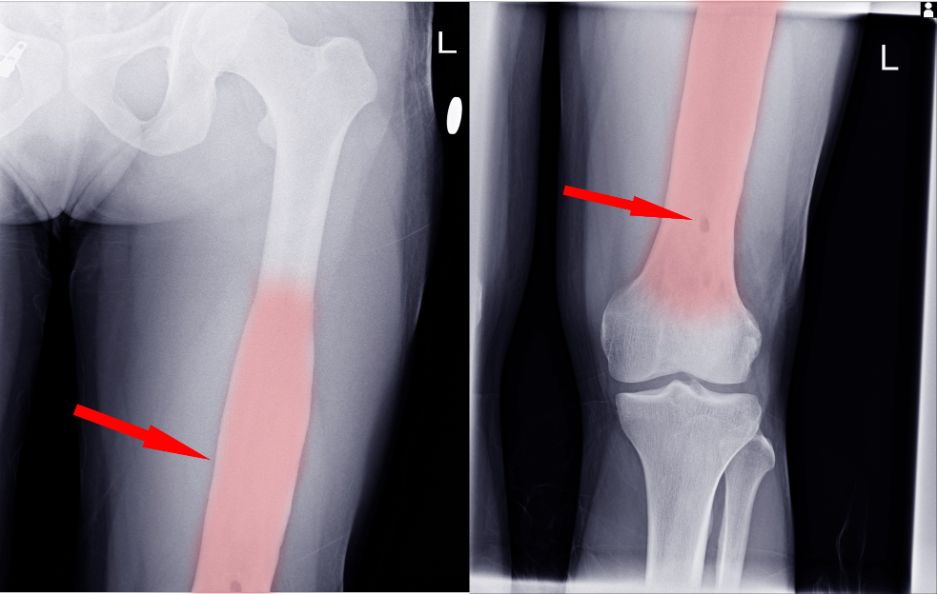
Osteosarcoma treatment depends on the stage of the disease. If you have a high grade tumor, it is more likely to spread to other parts of the body. The symptoms of high grade tumors can be very severe, including pain and fractures in the bone around the tumor.
If you have a low grade tumor, it is likely to remain in your bone and cause fewer symptoms. You will likely have to undergo radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or surgery to remove the tumor. Chemotherapy can also reduce the size of the tumor and reduce the risk of it spreading to other areas of the body. The cancer can spread to the surrounding blood vessels and nerves.
Chemotherapy is usually given before surgery, but it can also be used after surgery to help the surgeon remove the tumor more easily. Chemotherapy can shrink the tumor and kill cancer cells that have spread. You may also need radiation therapy, which uses beams that are directed to the osteosarcoma. Radiation therapy may also be used in combination with other types of treatment.
Osteosarcoma can be treated with radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or surgery. If you have osteosarcoma in your pelvis, jawbone, or spine, it may be harder to remove with surgery. If you have osteosarcoma that is located in another part of your body, your doctor may use a bone graft. This bone graft is made from bone from a different part of your body.