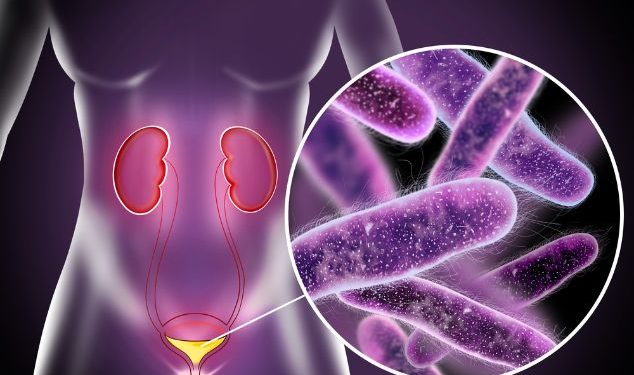
Urethritis is inflammation of the tube that carries urine out of your body (urethra). It usually happens in both men and women. Most people with urethritis have pain or itching when they urinate and an increased urge to pee. Some have no symptoms at all, called asymptomatic urethritis.
Symptoms of urethritis vary depending on the cause of the infection. The most common cause is a sexually transmitted infection, such as gonorrhea or chlamydia. Other causes include irritation from soap, lotion or deodorant. Experiencing trauma to the urethra can also lead to urethritis.
The condition can also be caused by a virus, such as herpes simplex virus 1 or 2. This virus can cause itching at the tip of the urethra and a discharge from your penis.
A swab of the inside of your urethra may be taken to test for an infection. The swab will be sent to a lab for testing. The doctor will also examine you and check for any swollen or tender tissue near your urethra. He or she may also take a sample of your urine for testing.
Treatment of urethritis typically involves a combination of antibiotics. The antibiotics will kill the bacteria that are causing the infection. In most cases, urethritis will clear up after the treatment is complete. However, if you do not get the antibiotics, the bacteria that cause the infection can stay in your urethra. This can cause you to have urethritis again in the future.
Antibiotics for urethritis are usually taken as pills twice daily, usually on an empty stomach. You will need to take these pills for about a week before you begin to feel better. It is important to finish all of the medication prescribed by your doctor.
If you are treated with antibiotics, it is important to follow up with your physician. The doctor will ask about your symptoms, how you are feeling and what is working for you. He or she can change your medicine if needed.
Treating a bacterial infection of the urethra is most often done by giving a single dose of ceftriaxone 500 mg intramuscularly, followed by a course of doxycycline 100 mg twice a day for seven days. The doxycycline should be stopped once symptoms are gone. A repeat test three months after treatment is recommended.
A DNA-based test is used to confirm the presence of gonorrhea and chlamydia in the urine. These tests can be done at your doctor’s office or hospital laboratory.
Prevention of urethritis is also very important. Avoiding sex and using condoms can help prevent the disease. In addition, you can also prevent it by using soap and other products that do not irritate the urethra.
The urethra is a very sensitive part of the body. This is why it’s so important to keep your urethra clean and dry. This helps prevent bacterial infections and other health problems. You should also avoid irritants such as soap and lotion that can clog your urethra.