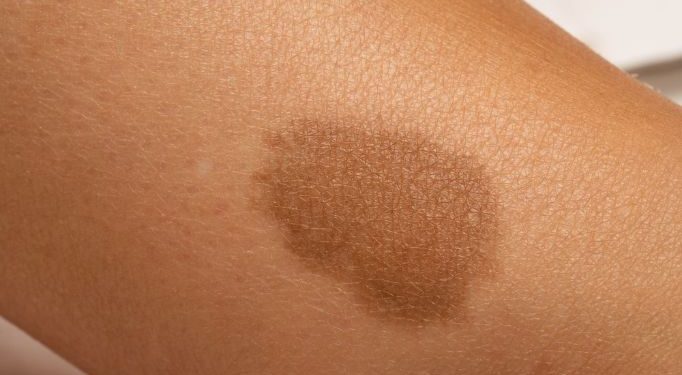
Hemangiomas are benign (non-cancerous) tumors made up of extra blood vessels that form in the skin, muscles or bones. Typically they are found on the head or face, but may also be seen in other parts of the body, including the chest, abdomen and back. They can occur in boys and girls, but are most common in girls.
Hemangioma symptoms are usually noticed by a doctor during a physical examination of the patient’s skin or lungs. Hemangiomas can be seen as small red bumps or spots on the skin that look like burgundy-colored birthmarks, or they may appear as large, swollen lumps in the muscles and lungs. Some hemangiomas can even be detected in an x-ray or MRI scan that is done for another purpose.
During infancy, hemangiomas grow rapidly and often become larger within the first 6 months of life. Most hemangiomas then shrink and disappear over time. However, some may bleed, swell or break through the skin.
Infantile hemangiomas, or strawberry marks, are the most common type of hemangioma in children. They are caused by an overgrowth of the cells that surround blood vessels in the skin and can be found on the face, scalp, chest or back. They usually fade and disappear by age 10.
Other hemangiomas are called internal hemangiomas and are most often found in the brain, spinal cord or meninges. These types of hemangiomas grow from the overgrowth of the cells around blood vessels in these membranes. They can spread to other areas of the body if they get too big.

The most common internal hemangiomas are hemangioblastomas and pilocytic astrocytomas. They are more severe than infantile hemangiomas and often require treatment.
Subglottic hemangiomas are large masses of blood vessels that can cause obstruction of the airway, typically below the vocal chords. They can also obstruct breathing and make it hard for the child to breathe normally.
They can be very painful and require medical attention if they cause breathing problems or interfere with other bodily functions. If they are found in the lungs, they may need to be removed surgically.
These hemangiomas can be very difficult to diagnose, and often need a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. Biopsies are performed under local anesthesia and involve taking a tissue sample from the area to be examined.
During the biopsy, your doctor will take a tissue sample to examine under a microscope. The cells will be analyzed for genetic markers that may be linked to the development of hemangiomas.
Hemangiomas can be treated by observation, medication, laser therapy and surgical removal. The best treatment depends on the location of the hemangioma, the size of the lesion, and your preferences.
Since 2008, the most common drug for treating infantile hemangiomas is an oral beta-blocker medication called propranolol. This medicine is given twice a day for at least six months. Alternatively, a topical medication called timolol can be applied to the hemangioma. Other medications used for more complicated hemangiomas include sirolimus or vincristine.