Upper respiratory tract infections (URIs) are illnesses that affect the nose, sinuses, throat, and voice box. They are usually caused by viruses. Most people recover on their own without antibiotics.
Symptoms of an upper respiratory infection can range from the common cold to serious issues such as pneumonia. It is important to get medical attention if you or a loved one develops any symptoms of an upper respiratory tract infection such as fever, sore throat, cough or a runny nose.
How do these infections spread?
A URI is a common health problem that can affect anyone at any time. Typically, these infections are caused by viruses and usually resolve within a few weeks.
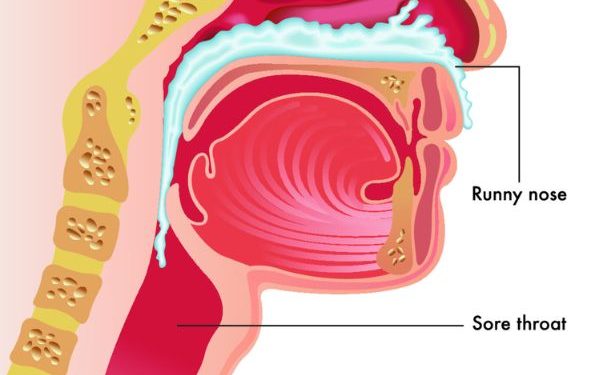
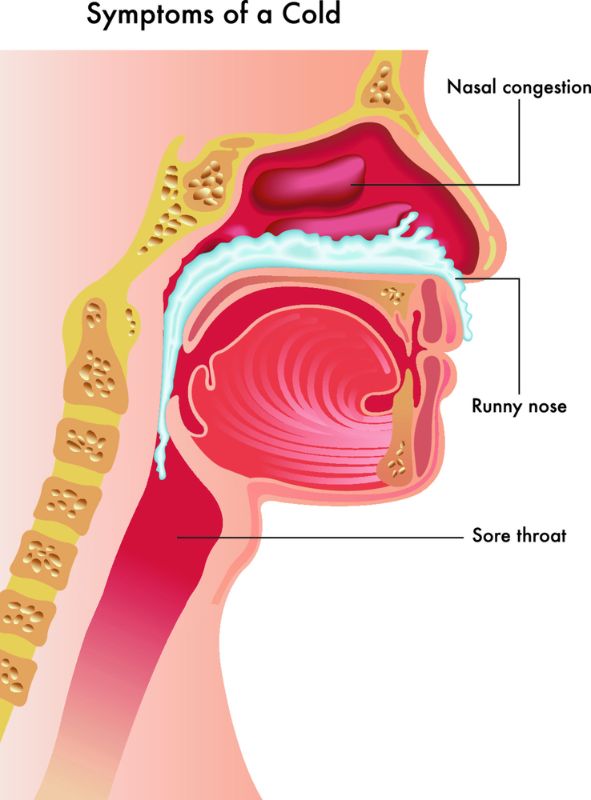
The most common symptoms of an upper respiratory infection are congestion, a runny nose, sore throat, cough and mucus production. You may also experience headache, body aches, and fatigue.
What is the difference between a cold and the flu?
The cold is a viral illness, while the flu is a bacterial infection. Both illnesses cause similar symptoms, but the flu has more severe symptoms such as a high temperature and muscle aches.
What can I do to prevent an upper respiratory infection?
A healthy lifestyle, such as regular handwashing, avoiding close contact with people who are sick, and staying home when you feel run down can help prevent a URI. It’s also a good idea to get the flu shot each year.
Why are a lot of people sick?
Viruses enter the upper respiratory tract through your nose and then pass through the airways, where they can spread from person to person. This happens most often when someone sneezes or coughs and doesn’t cover their nose or mouth.
It’s important to note that a cough is the body’s way of fighting germs, so it’s not necessarily the source of the infection. However, if you have a cough that lasts more than two days, it’s important to see your doctor.
If you have a cold, take it easy and stay home. Try to rest and drink lots of fluids. You may also want to use pain relievers or antihistamines to make your symptoms less intense.
Your healthcare provider can give you medicines such as cough suppressants and saline solutions to reduce symptoms. They can also prescribe an antibiotic to treat a bacterial infection such as strep throat.
Treatment of an upper respiratory infection depends on the type of URI you have. Symptoms of an upper respiratory infection generally start 1-3 days after you come into contact with the virus and can last 7-10 days.
Bacterial URIs are more likely to cause a severe disease such as pneumonia or bronchitis than viral URIs. If you have a bacterial infection, you can be given an antibiotic such as penicillin or amoxicillin.
A child with a bacterial upper respiratory infection such as strep throat can have a fever, cough and a sore throat. Your healthcare provider will diagnose your infection by reviewing your symptoms, physical exam and sometimes laboratory tests.