Nasal and sinus diseases symptoms vary according to the cause, but most sinus infections can be cured with simple self-care measures, medical treatment and avoiding things that irritate your nose. Symptoms of nasal congestion and drainage can include a runny nose, cough, fever, sore throat and facial swelling.
Headaches can also be a sign of sinusitis. They can be a dull, constant pain that occurs on the bridge of your nose or around the front and back of your eyes. This pain can be worsened by the change in barometric pressure or by changing your sleeping position.
Your symptoms may start when you are sick or have a cold, and they may last up to 7 days or more. If they aren’t relieved by over-the-counter pain medicine, you should visit your doctor for a diagnosis.
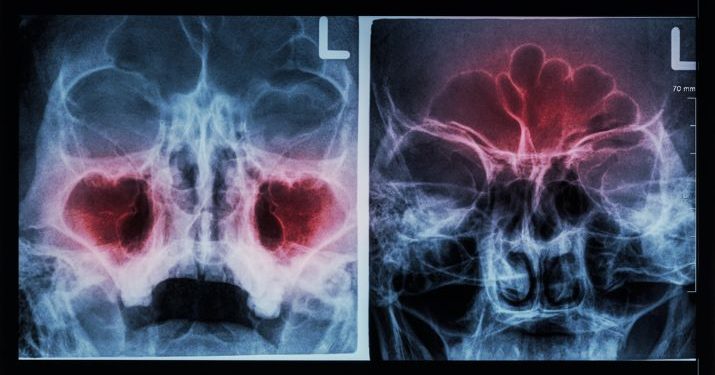
Sinusitis is an inflammation of the lining of your sinuses, which are hollow areas within the bones of the face that are connected to your nasal passages. It is often caused by viruses, but it can also be a result of bacteria and sometimes fungus.
The symptoms of sinusitis are characterized by nasal congestion, facial pain or pressure, and a discharge from the nose that is thick green or yellow. These symptoms usually go away after a few days, but they can continue for longer periods of time in chronic sinusitis.
There are two main types of sinusitis: acute and chronic. Acute sinusitis is short-term (less than four weeks) and usually caused by a virus, while chronic sinusitis is long-term (more than 12 weeks) and most often caused by bacteria.

Acute and chronic sinusitis are usually accompanied by other symptoms, such as a bad headache, facial aches and tooth pain. These other symptoms can be confused with the typical flu or upper respiratory infection, so you should see a doctor to get a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Your doctor can diagnose sinusitis using a detailed history and physical examination. He or she can determine whether your mucus is purulent and can look at your sinuses with a microscope to help distinguish bacterial from viral sinusitis.
Complications of a sinus infection are rare and are more likely to happen in children than adults. The most common complication is orbital extension, which occurs when a chronic infection moves into the area surrounding your skull. This can lead to brain and eye infections, or even meningitis.
You can prevent sinusitis by avoiding cigarette smoke, polluted air, and other things that irritate your nasal passages. If you have allergies, managing them with medications and other treatments can also decrease your chances of developing this condition.
Drink plenty of fluids to thin the mucus and keep it from blocking your sinuses. Warm compresses can also help reduce the swelling and pain associated with a sinus infection.
Avoiding alcohol can help reduce the severity of your symptoms, as it irritates your nose and mucous membranes. Medications can help control these symptoms, but they should only be used as prescribed by your doctor.