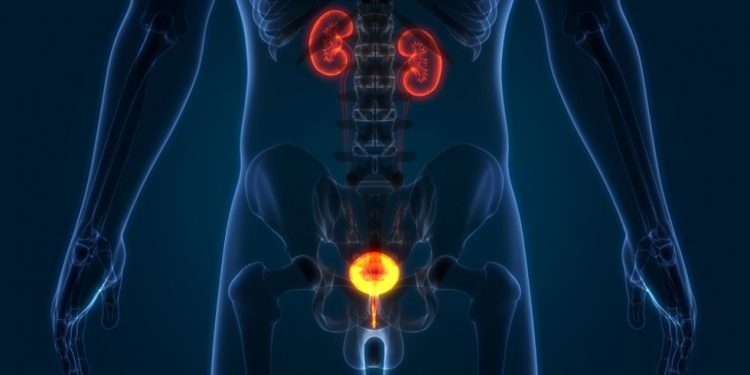
Prostate cancer is a common condition that occurs when cells in the prostate gland grow out of control. These cells can stay in the prostate or spread to other parts of the body. The condition can occur at any age, but is most common in men over the age of 50.
Stage 4 – Advanced Prostate Cancer
The most serious type of prostate cancer is called stage 4. It is diagnosed when cancer cells have spread beyond the prostate to other areas of the body, such as the bones or lymph nodes.
This is where your treatment team will work together to determine what treatments are best for you. They will also help you make decisions about pain management, symptom relief, and quality of life.
Treatment options for stage 4 include surgery, hormone therapy, radiation, and chemotherapy. You may also need immunotherapy, a vaccine therapy that can boost your immune system to fight cancer.
Your doctor will use a combination of tests and scans to determine your stage. This information will help your doctor plan your treatment and determine how aggressive your cancer is.
For instance, if you have an advanced tumor that has spread to your bone, it will be more difficult to treat. Fortunately, there are newer treatments that can target this type of prostate cancer and ease your symptoms.
Hormone therapy helps to suppress the growth of the cancer. It can be used alone or in combination with other treatments, such as radiation therapy. This can improve your short-term and long-term chances of survival.
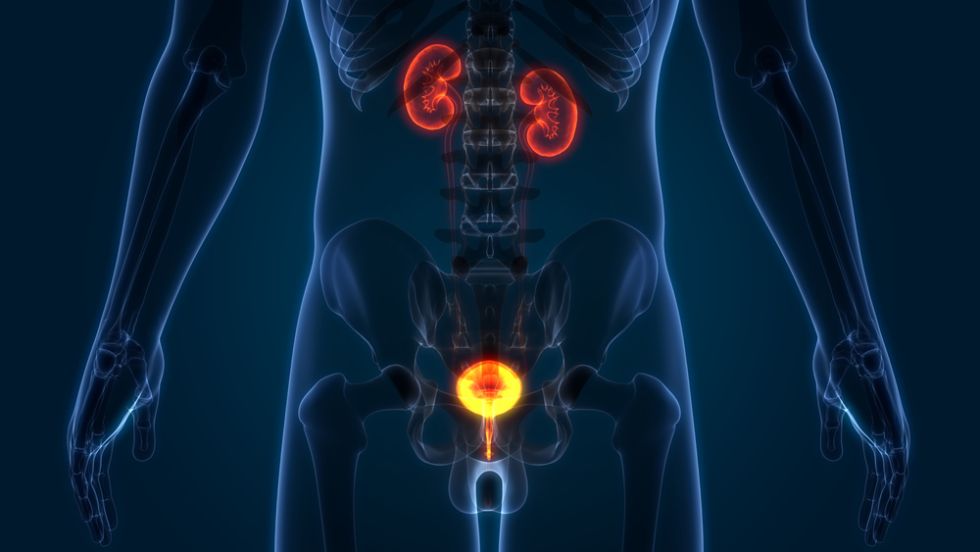
Radiation therapy uses high-powered beams of energy, such as X-rays and protons, to kill the cancer. It is often given in a large machine that moves around your body, delivering the radiation to the cancer area.
The type of radiation you receive depends on the location and size of your tumor, as well as your overall health and other factors. Your doctor may recommend a different kind of radiation treatment than the one you had previously.
In addition to the type of radiation you receive, the location and size of your tumor will also affect how effective it is. Generally, a larger tumor is more likely to respond to radiation.
If you have an advanced cancer, your doctor will decide if you should undergo surgery to remove the cancer. This can be done by either removing the entire prostate gland (radical prostatectomy) or by a more minimally invasive procedure called a transurethral resection of the prostate, or TURP.
Your doctor may also recommend a hormone therapy to manage your symptoms and relieve pressure on the bladder. This can help reduce your erectile dysfunction, hot flashes, and loss of bone mass. It can also reduce your sex drive, breast enlargement, and weight gain.
You will have regular checkups with your doctor to keep track of how you are doing. Your doctor will take your blood and urine samples and examine you for any signs of cancer growth.