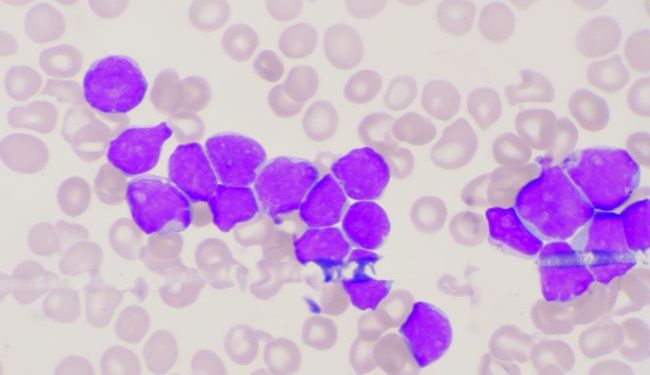
While there is no known cause for lymphatic cancer, it is a type of blood cancer that causes swelling of the lymph nodes. Lymphoma develops when there is a genetic mutation in the white blood cells. This mutation signals the cells to multiply rapidly, allowing the diseased lymphocytes to continue living. Too many of these cells can spread throughout the body, causing swelling of lymph nodes. Although there is no known cure, it is possible to reduce the chances of developing lymphoma.
Normally, the lymph nodes are tiny, bean-like structures. These organs serve as reservoirs for microorganism-fighting antibodies and traps waste materials. They are connected to one another by milk-colored tube-like vessels. Lymphoma develops when white blood cells begin to proliferate abnormally and form masses. Some lymphomas even affect the bone marrow, causing a reduced red blood cell count.
When lymphoma develops in the lymph nodes, the symptoms are similar to those of a common viral infection, but they may continue for a prolonged period. Lymph nodes are found throughout the body, and swelling of them is common. Sometimes, the swelling is painless, but it may become painful when the enlarged glands press on organs or bones. Patients suffering from lymphoma should visit a doctor as soon as possible, as it may severely limit their quality of life.
Although lymphatic cancer can be a terrifying diagnosis, treatment for the disease is effective. With proper diagnosis, lymphoma patients can live long lives. With the right treatment, lymphatic cancer patients can expect to experience a life free of recurrence. There are many options for treatment, including surgery, radiation therapy, and targeted therapies. Fortunately, a lot of patients with lymphoma have successfully completed treatment.
Patients with lymphoma can undergo several diagnostic tests. A physical exam will help doctors identify whether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes, while an imaging test may detect cancer in specific areas of the body. A bone marrow biopsy, for example, can show whether the cancer has spread to bone marrow or outside the lymphatic system. In some cases, a lymphoma diagnosis can be made without surgery. If the cancer has spread outside of the lymphatic system, it is often less deadly than other forms of cancer.
Although a diagnosis of lymphoma is based on the severity of symptoms, treatment may be different depending on the type and location of the lymph nodes. The lymphatic glands contain different kinds of lymphocyte cells. In the low grade stage, the lymphoma grows slowly and produces only minor symptoms. In contrast, aggressive lymphomas spread throughout the body, resulting in more pronounced symptoms. However, the good news is that most cancers can be treated.
Children with lymphatic cancer are at an increased risk of developing the disease. It’s the third most common cancer in children under the age of 15, behind only leukemia and brain tumors. In addition to causing symptoms and amputations, lymphatic cancer can lead to life-threatening infections, such as sepsis. However, it is important to note that a diagnosis of lymphoma is crucial to a patient’s survival.