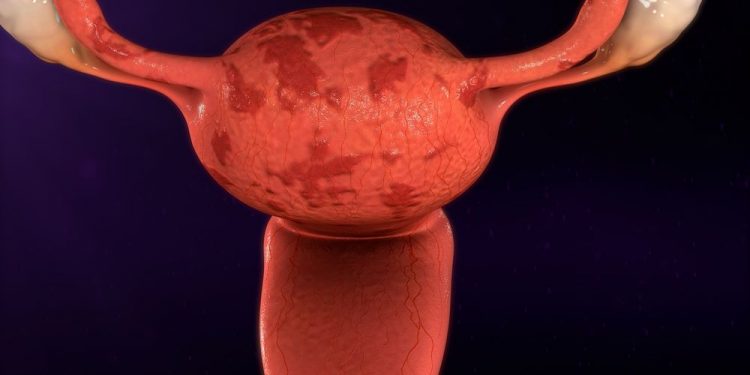
Uterine leiomyoma are growths made up of muscle and fibrous tissue from the wall of the uterus (womb). They’re not cancerous (benign) and most women over 35 develop them. They can cause heavy or abnormal uterine bleeding and pelvic pain and can have an impact on fertility. They also have an economic impact on health care systems of approximately 34 billion dollars a year in the United States alone.
The uterus is an upside down pear-shaped organ in the pelvis which is the main site for a woman’s ovulation and development of pregnancy. It is the place where a baby grows during pregnancy and is a vital part of a woman’s reproductive system. The uterus is the largest organ in the female pelvis and is about the size of a lemon.
Fibroids can be found in different parts of the uterus and can vary in their size. The fibroid’s size and location can have an effect on symptoms, as well as the patient’s quality of life. The symptom that is most common in women with uterine fibroids is abnormal uterine bleeding. Other symptoms may include pelvic pain, a feeling of fullness in the abdomen, constipation and frequent urination. In extreme cases the uterus can grow so large that it can press on the bladder and diaphragm.
It’s important to know that most uterine fibroids are not cancerous and will not become cancerous. However, there are some fibroid tumors that can transform into a cancer called a leiomyosarcoma, which is more serious and needs to be treated immediately.

Fibroids are most commonly located inside the uterus, but they can also be found on the outside (endometrial surface) of the womb or within the endometrial cavity. The location and size of the fibroid can influence the type of treatment that will be recommended.
Most often a fibroid is diagnosed by a gynecologist during a gynaecological examination or pelvic ultrasound. Occasionally they’re discovered during other types of medical procedures, such as a hysteroscopy where a thin telescope is used to examine the uterus or laparoscopy where a small cut is made in the abdomen and a surgical instrument is inserted.
There are a number of treatments for uterine fibroids. These include a fibroid embolization procedure that involves inserting a catheter in the uterine artery or radial artery and then using specialized tools to block blood flow to individual fibroids, which shrinks them and relieves symptoms. There are also medications that can be taken by mouth or intravenously to help reduce uterine fibroids. Ultimately, surgery remains the most successful method of treating uterine fibroids and has historically consisted of either a hysterectomy or myomectomy. For many patients, however, a hysterectomy can be associated with significant health and social consequences and is not always necessary. Various newer minimally invasive procedures are available and are being evaluated in clinical trials.