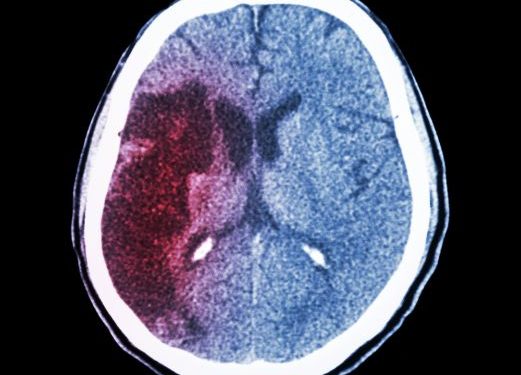
Surgical intervention, called a colectomy, removes the infected portion of the colon and adjacent tissue, such as the lymph nodes, to minimize the likelihood of cancer spreading. The surgeon will also create a new path for the waste to exit the body. After the surgery, a flat bag is placed over the stoma, or opening, in the abdominal wall.
Early detection of colon cancer is important, as a few polyps do not show any symptoms. However, early detection of polyps greatly improves the prognosis. While only four out of 10 polyps are detected at an early stage, early diagnosis leads to less invasive treatments and increased survival rates. But what are the best methods of treatment for colon cancer? A combination of lifestyle choices and screenings may reduce your risk.
There are many stages of colon cancer, and the exact path to treatment depends on where and how far the cancer has spread. This system is based on the TNM staging system, which describes cancer in stages based on where it has spread. Stage 0 colon cancer is called carcinoma in situ and is usually small and easy to treat. Stage 1 cancer has spread beyond the colon but has not yet invaded lymph nodes.
In addition to surgery, chemotherapy may be necessary for the treatment of colon cancer. These drugs are given through the vein and may be combined with other treatments. Radiation therapy is another form of cancer treatment. It uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. The doctor determines the best treatment plan for your individual case. Sometimes, patients may opt for no treatment at all, which can also lead to colon cancer spreading to other organs. In the worst case scenario, you may even end up with a complete bowel obstruction or a perforated intestine.
In the majority of cases, colorectal cancer starts out as a benign polyp in the inner lining of the colon. However, there are a few types of colorectal cancer that develop into cancer. If you catch it early enough, you can treat the condition before it progresses. Most colorectal cancer treatments can be cured. If detected in its early stages, however, there are still many treatments available.
While surgery is the best way to prevent the disease, colon cancer cannot be prevented entirely. Regular screening is important, especially if you have a family history of the disease. Genetic damage to specific genes can cause uncontrolled cell growth and make colon cancer more likely to develop. Even though most cases of colon cancer are found in people over the age of 50, the risk is increasing among younger adults. A sedentary lifestyle, excessive consumption of red meat, alcohol, and unhealthy diet are all risk factors.
When colon cancer has spread beyond the rectum, it has penetrated the mucosa and muscle layer. It has also spread to nearby tissues and lymph nodes. However, colon cancer has not yet spread to other parts of the body. This indicates that the disease has not spread far enough. Once this stage has occurred, the cancer will likely spread to other organs and tissues. Surgical treatment for colon cancer is aimed at preventing it from spreading.