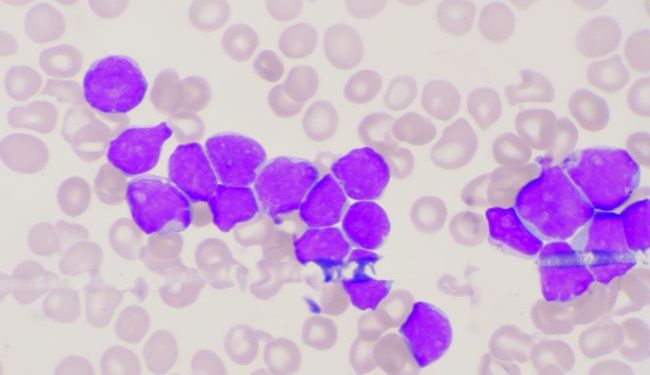
The disease affects the bone marrow, which produces a wide variety of blood cells. The cells in the bone marrow carry oxygen to all organs and cause anemia, which can cause fatigue and shortness of breath. Another symptom is low blood platelets, which are important for clotting in the body’s blood. Patients with this disorder will have a weakened immune system, making them more susceptible to infection.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia symptoms occur in a person who has an excessive number of immature white blood cells. They develop slowly over a few weeks, becoming more severe as the number of abnormal white blood cells increases. If you notice any of these symptoms, consult your doctor to make sure they’re not due to something else. However, it is important to be diagnosed and treated as soon as possible.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia is a disease of the blood that affects the white blood cells. The abnormal white blood cells accumulate in the blood and bone marrow, crowding out healthy blood cells and making it difficult for them to do their jobs. In extreme cases, the condition can lead to fatal complications. For this reason, it is essential to seek treatment as soon as possible. While the disease is incurable, there are certain symptoms that will be visible at the first sign of the condition.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia is characterized by a high number of immature white blood cells. As the number of these cells rises, the symptoms of Acute Myeloid Leukemia will increase. This is especially true for pregnant women and children. The initial feeling of illness is often caused by an infection, rather than by AML. While leukemia causes the immune system to attack germs, normal white blood cells cause the initial fever. In addition to the symptoms associated with AML, people with this condition may also experience recurring infections.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia symptoms are often difficult to detect. A diagnosis is based on the presence of characteristic symptoms. A thorough clinical evaluation and a detailed patient history are required to make a diagnosis. Acute Myeloid Leukemia symptomatic patients are often referred to an oncologist for diagnosis and treatment. Acute Myeloid Leukemia is a type of cancer of the white blood.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia symptoms develop over a few weeks and get worse as the number of immature white blood cells increases. It is important to seek a diagnosis as early as possible, as symptoms of AML may be a sign of other illnesses. Acute Myeloid Leukemia symptomatic meningitis is a serious condition that can cause serious complications.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia is a cancer of the white blood cells that start in the bone marrow. It is very rare in the adult population and typically occurs in young children. Acute Myeloid Leukemia is usually asymptomatic, but can develop in the periosteum. When it is metastatic, it can spread throughout the body and cause a wide variety of symptoms.
The main symptoms of AML include low blood cells. Low blood cell counts may result in anemia, shortness of breath, and a pale appearance. In addition, a low platelet count may result in frequent, prolonged bleeding from minor cuts and bruises that have no apparent cause. Joint pain is another symptom of increased leukemia cells. In addition to these, AML may also result in joint pain, so it is essential to visit your physician.