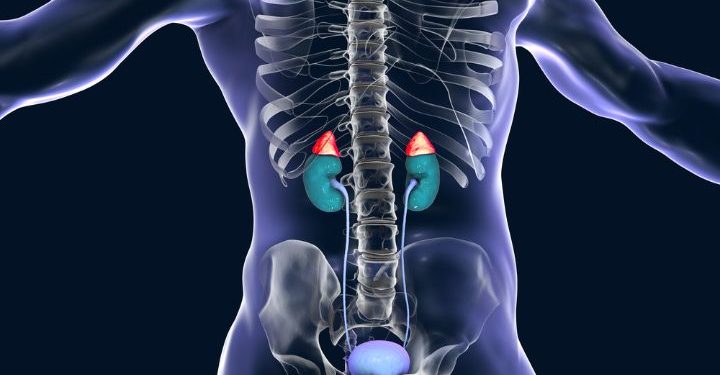
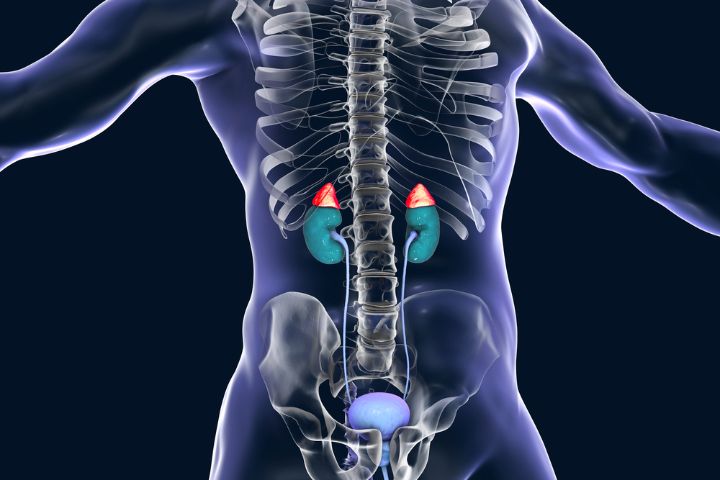
Adrenal Gland Disorders symptoms are the body’s response to problems with your adrenal glands. These glands produce hormones that control your heart rate, blood pressure and breathing. When the glands are not working properly, it can affect your entire endocrine system.
When the pituitary gland doesn’t send proper signals to your adrenal glands, your adrenal glands can produce too little or too much of these hormones. These imbalances can lead to a number of health issues.
Some of these imbalances are caused by disease, infections, tumors or other conditions that affect your endocrine system. Others are the result of problems with your hypothalamus (a part of your brain) or your pituitary gland that regulates the hormones that your adrenal glands make.
Cushing’s syndrome, a condition that causes your adrenal glands to make too much cortisol, is one of the most common types of adrenal disorders. Treatment for this condition involves steroid medications, but it can also be curable with surgery.
Addison’s disease, also known as adrenal insufficiency, is a condition that occurs when your adrenal glands don’t make enough of the hormone cortisol and/or aldosterone. This condition can cause high blood pressure, low potassium levels in the blood, and other problems.
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is an inherited disorder that prevents your adrenal glands from producing cortisol and other hormones. This disorder can be very serious.
Pheochromocytoma/paraganglioma is a rare form of adrenal tumor that develops in the medulla (the outer layer) of your adrenal gland. This tumor is usually noncancerous, but it can cause an overproduction of hormones that can affect your heart rate and blood pressure.
Hyperaldosteronism is another type of adrenal disorder that happens when your adrenal glands produce too much of the steroid hormone aldosterone. This causes your blood pressure to rise and can lead to potassium loss in the blood.
Virilization is another symptom of adrenal gland disorders that can affect your sex hormones. This condition occurs in females or boys before they reach puberty and can be very dangerous.
Some of these symptoms are similar to other diseases or problems, so it’s important to see your doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment. Your doctor may need to run tests and get X-rays or CT scans of your abdomen to determine the cause of the problem.
If your doctor suspects you have an adrenal disorder, they will prescribe medication and/or check your blood or urine levels of hormones. They may also want to do a tomography scan or an MRI to look at your adrenal glands.
Tumors are often a sign of an adrenal disorder. Tumors can disrupt hormone production, but they are usually noncancerous and can be treated with medicine or surgery.
About 1 percent of people have a mass or nodule that is growing on the surface of their adrenal glands. This is called an “adrenal incidentaloma” and it is most often found during an examination for some other condition.
Fortunately, most asymptomatic adrenal nodules don’t cause any health problems. However, these growths may need to be ruled out when your doctor orders an imaging test for another reason.