Autoimmune hepatits (AIH) can be a lifelong condition that requires regular monitoring and treatment. A good outcome is possible in about seven out of 10 people who start treatment.
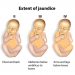
Symptoms of AIH range from mild to severe and can develop gradually over time or quickly in acute attacks (acute hepatitis). Many people don’t notice symptoms until they are diagnosed with the disease, but others may develop them.
A blood test can help diagnose autoimmune hepatitis. It measures the amount of a specific type of protein in your body called immunoglobulin G. This type of protein helps your body fight infection and inflammation. It’s higher in people who have autoimmune hepatitis than it is in people who don’t have the disease. A liver biopsy is also helpful.
The doctor may also recommend other tests to help make a diagnosis. These include a liver ultrasound, which uses high-frequency sound waves to see inside your liver. This can show how much swelling and scarring has occurred. The doctor can also take a sample of liver tissue to look at under a microscope and get a better look at the cells involved in the inflammation.
Liver damage caused by autoimmune hepatitis can progress over time to inflammation, scarring and liver cirrhosis. If left untreated, these conditions can lead to liver failure and death.
Your doctor will perform a series of specialized blood tests to find out if you have autoimmune hepatitis. These tests can identify AIH by looking for certain antibodies that help your body fight infection and inflammation, and they can check the health of your liver.
If you have autoimmune hepatitis, the most important thing is to treat it with medication that can keep your immune system from attacking your liver. Most patients need a long-term course of prednisone, a type of steroid that suppresses your immune system and helps control the inflammation in your liver. In addition, your doctor usually prescribes azathioprine, an immunosuppressant drug that can allow you to take lower doses of prednisone.
Medications are most effective when they’re started early and are given on a regular basis. These medications can be combined with other treatments or lifestyle changes to promote healthy liver function and minimize the damage that occurs from this chronic disease.
In some cases, treatment for autoimmune hepatitis can reverse the effects of the disease and reduce the amount of swelling and scarring in your liver. However, it’s important to follow up with your doctor regularly and be careful about your diet. Your child’s hepatitis specialist can provide information on which foods to eat or avoid and other lifestyle changes that can prevent the symptoms of this disease.
The treatment for autoimmune hepatitis depends on the stage of the disease and your personal health history. For most people, the condition goes into remission with treatment and becomes less severe in a few years.
The hepatitis specialists at NewYork-Presbyterian’s Center for Liver Disease and Transplantation can help you with treatment for this serious liver disease. You can learn more about your options and how to manage this condition at our website.