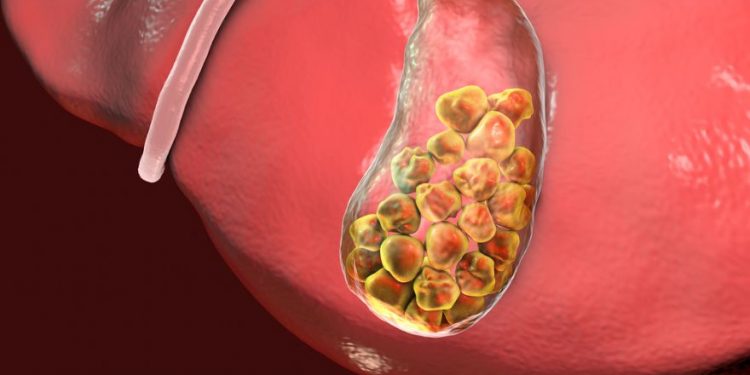
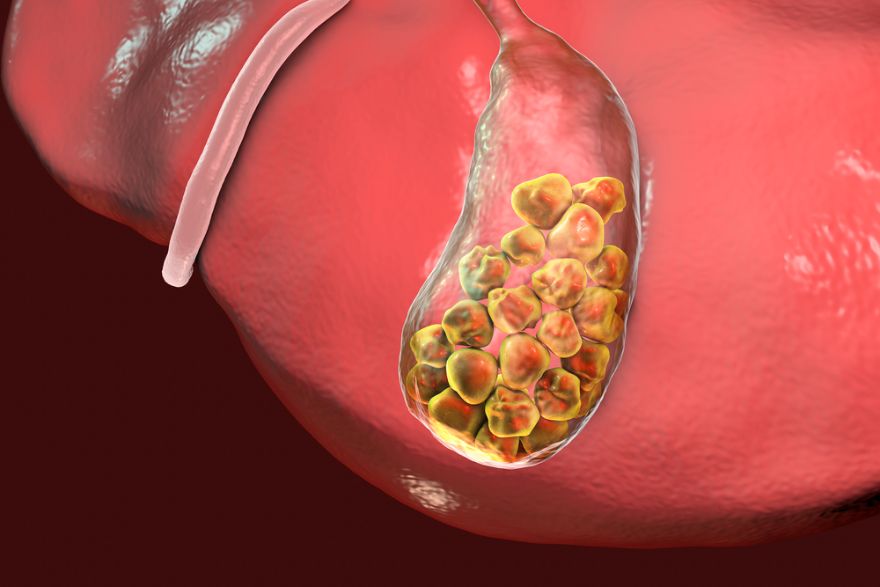
biliary atresia is an illness that affects infants. It is caused by scarring of the biliary tree, which is a series of tubes in the liver that drains bile. The disease may result in jaundice, which is a yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes. Other symptoms include pale yellow stools and blood tests that show abnormal liver function. The condition can be very serious, and can cause cirrhosis.
The disease usually occurs in the first two weeks of an infant’s life. When the baby’s liver is damaged, it cannot produce enough bile, which is necessary to digest fats. As bile accumulates in the liver, the liver becomes enlarged and hardened. This makes it harder for bile to drain into the intestines, which impairs digestion and growth. The enlarged liver can also lead to scarring, which can lead to cirrhosis and other liver diseases.
When a doctor suspects biliary atresia, he or she will take a blood sample from the infant. The sample will be examined by a pathologist. The pathologist will look for signs of damage to the liver. If he or she is able to find any damage, a liver biopsy will be performed. The biopsy will involve taking a tiny sample of liver tissue. This sample is examined under a microscope to look for signs of disease. If the sample indicates that the baby has biliary atresia, then a diagnosis is likely.
If the baby has been diagnosed with biliary atresia, the condition may be treated with surgery or with a liver transplant. The Kasai procedure is the primary treatment, and it is most effective in babies under three months of age. If the child does not have a liver transplant, he or she will have to have regular monitoring of his or her health. Other types of treatment include high-calorie liquid feedings and MCT oil, which is used to increase digestive capacity.
If the baby is not gaining weight, a health care professional will likely recommend that he or she eat a lot of calories through a nasal tube. Alternatively, the child may be given a high-calorie liquid feeding through a tube in the esophagus. These high-calorie liquid feedings may be necessary if the child is too sick to eat. In some cases, the child may have to take MCT oil, which contains medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), in addition to regular vitamins and food. This type of treatment may help to prevent the child from developing malnutrition.
A diagnosis of biliary atresia will be confirmed with a liver biopsy, which will involve taking a small sample of liver tissue from the child’s liver. The pathologist will examine the sample under a microscope to find out if it is likely that the baby has the disease. Then, he or she will talk with the family about the possibility of a liver transplant. This procedure is a major surgery and will require that the child have frequent follow-up visits with a pediatric surgeon.