Blastocystis hominis is a microscopic parasite that inhabits the human digestive tract. Symptoms include watery diarrhea, abdominal pain, and constipation. A diagnosis of blastocystis hominis is made when there is a presence of the organism in the feces. However, this does not always mean that the patient is infected with the parasite. Depending on the person’s gastrointestinal health, symptoms may be mild or severe.
Blastocystis hominis may be passed from person to person through the feces. This infection is more common in people living in countries with poor sanitation. People with weakened immune systems also have a higher chance of being infected. In addition, travelers in developing nations should avoid eating uncooked foods. Symptoms can develop quickly and last for several months to a year. If you have questions about the illness, seek the advice of a medical professional.
The symptoms of Blastocystis hominis can be similar to those of other infections. You may experience abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, and weight loss. While the disease can be treated, its symptoms can last for months. Symptoms may not be obvious until weeks after the initial attack, which can make diagnosing the condition difficult.
Blastocystis is commonly picked up through infected food, water, and surfaces. It is often associated with other illnesses that are caused by viruses and bacteria. As with other diseases, a patient may be infected with a more virulent microbe. Patients can suffer from symptoms such as cramps, abdominal pain, and itching.
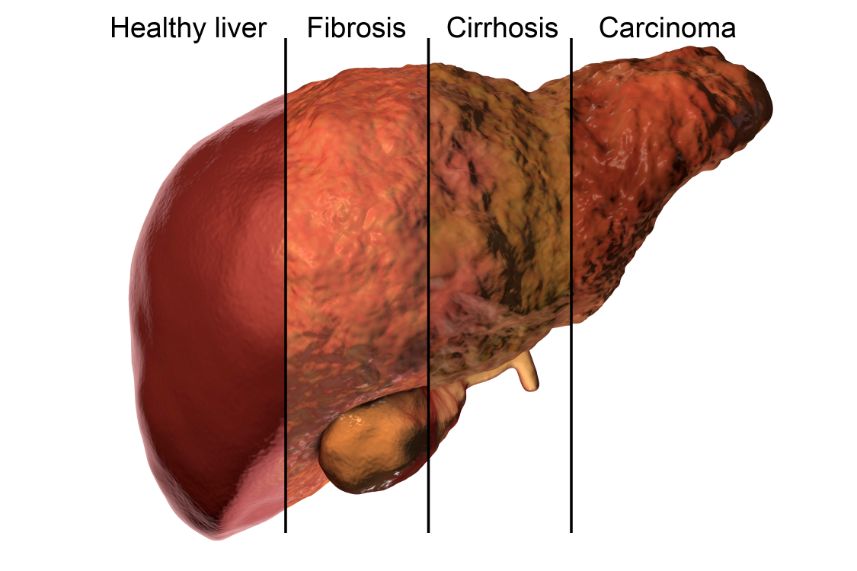
When the disease is diagnosed, there are several tests that the physician can use to determine the type of pathogen that is causing the symptoms. Some of these tests are fecal examination, endoscopy, and blood tests. Blood tests can help to rule out other causes of gastrointestinal symptoms. Other forms of testing may only reveal parasite activity.
After a diagnosis is made, a physician can treat the patient with medications. Most treatment options involve antiprotozoal drugs. Antiprotozoal drugs are not always effective in treating blastocystis. Medications that work on other parasites can also be effective on blastocystis. These medications include acyclovir and doxycycline. Alternatively, a combination of the drugs can be used.
Symptoms of blastocystis can last for months or even years. They include abdominal pain, abdominal distention, constipation, loose or watery stools, and abdominal itching. Oftentimes, patients will be unable to pass the parasite out of the body. This can lead to bowel obstruction and colonic ulcers.
Blastocystis ‘hominis’ is a parasite that can live in the intestines of people with chronic diarrhea. Blastocystis ‘hominis’ can also be found in recreational water, such as swimming pools, hot tubs, and sewage from humans.
While there are no vaccines for B. hominis, it is still recommended that those who have weakened immune systems seek the advice of a medical professional. Also, those who have traveled to areas with poor sanitation are at higher risk for being infected with the parasite.
Although Blastocystis is an infectious organism, it is not usually transmitted to other animals. Previously, the bacteria was considered to be a normal part of the gastrointestinal flora of the human body.