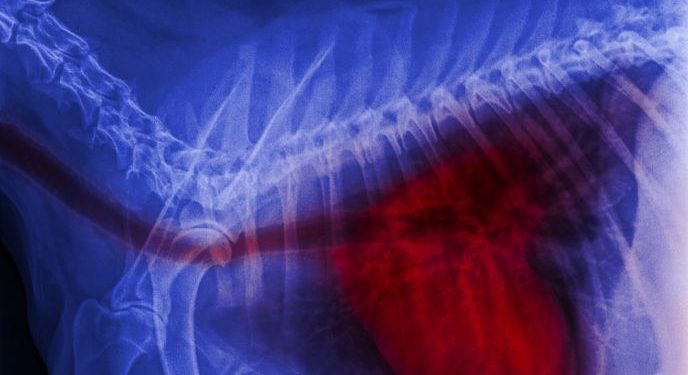
Blastomycosis is an infection caused by the fungus Blastomyces dermatitidis. This fungus can cause inflammation to the skin, bones, and organs. The symptoms of this disease can include fever, cough, and pain in muscles and joints. A person can get blastomycosis from breathing in the spores of the fungus, or by being contaminated by the spores. These spores can spread to the lymphatic system, or other organs.
Symptoms of this disease may appear as soon as three months after the fungus is first breathed in, but the disease usually progresses slowly and does not always show up right away. However, if you experience these symptoms, it is important to seek medical help.
During the initial stages of blastomycosis, symptoms may be similar to those of a flu infection. If your symptoms become severe, you should see your physician immediately. You may have to have a blood or urine sample drawn to find out if you are infected. An enzyme immunoassay can be used to test your urine for fungi. Typically, a physician will collect a tissue biopsy of the affected part of your body. Depending on the sample collected, the physician can then use a commercial DNA probe to verify the presence of the fungus.
Blastomycosis is most common in the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. In some cases, the infection can spread to the brain. It can also lead to meningitis or epidural abscess. Patients with blastomycosis often have a weak immune system, and they will require close monitoring to prevent a relapse.
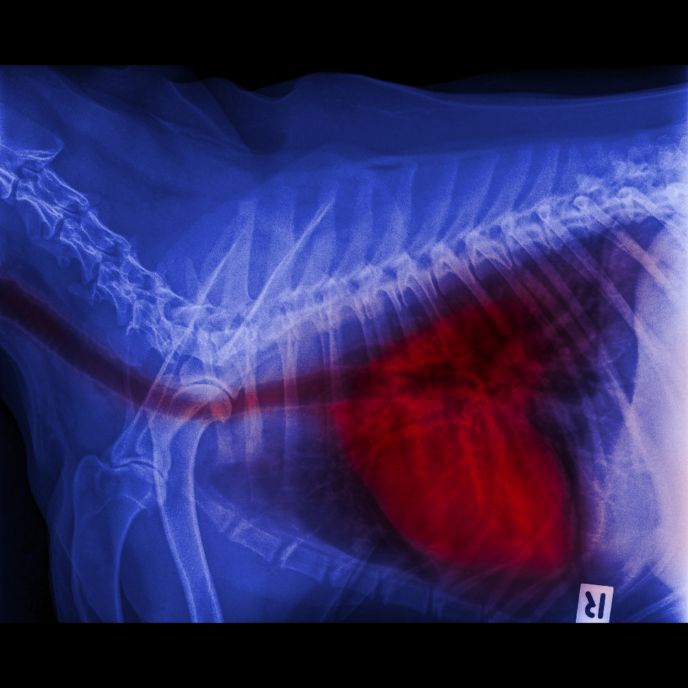
The disease can be fatal if left untreated. Patients with an infected animal in their home are at an increased risk of developing the disease. Although a cure is not available, some patients have a good prognosis. They can be treated with azole drugs like terbinafine, voriconazole, and itraconazole.
As with humans, the fungus can also infect animals. Usually, the disease is found in areas of Africa and the United States, but it can occur in areas of India. When an infected dog is brought into the household, there is an increased chance that other household members will become infected. To avoid this, it is vital to follow strict hygiene practices when handling your pet. Also, make sure to wash your hands after touching an infected dog.
The most common sites where this infection can occur are the lungs, skin, and bones. While the fungus can be transmitted by direct contact, it can also be passed on through the blood or by breathing in spores. Symptoms can be very similar to those of other diseases, including TB.
Symptoms of this disease may start as a skin lesion, with the appearance of irregular wartlike papillae or bullae on the surface. The lesion might heal into an atrophic scar or it may become swollen. Abdominal masses can also develop and the patient’s abdomen might become painful. There are also cases of purulent subcutaneous collections that result in chronic discharging sinuses.