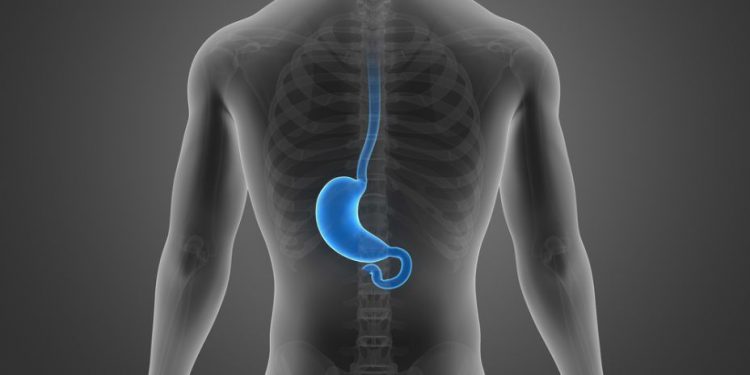
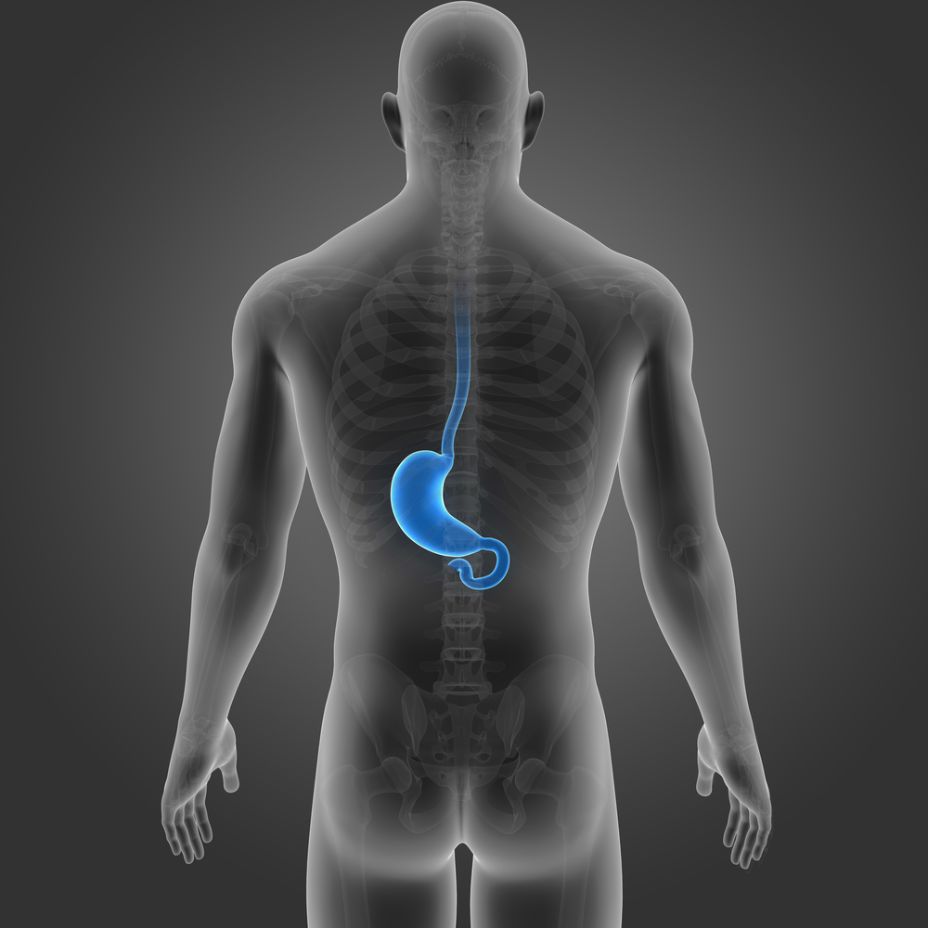
The cervical esophagus extends from the cricoid cartilage to the thoracic inlet. It is located in the pre-thoracic region of the digestive tract and is the first part of the esophagus to extend beyond the yolk sac. It is an important embryological structure and develops into a digestive tube through the migration of cells from the extraembryonic portion to the intra-embryonic portion. Carcinoma of the cervical esophagus is less common than squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus. Historically, this type of cancer has been treated with surgical resection but these tumors are difficult to operate on due to the close proximity of the structures around the cervical esophagus.1
Surgical resection can result in a permanent tracheostomy, and the survival rates are lower than those of thoracic esophageal cancer. Recently, however, a number of institutions have reported good outcomes with chemoradiation therapy.
A patient’s treatment will be determined after a thorough pre-treatment evaluation. Typically, this will include a CT or MRI scan, chest or dental X-rays and blood work. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the most common treatments for cervical esophageal cancer involve surgery, radiation and chemotherapy.
Surgery involves removing the tumor from the cervical esophagus and reconstructing the esophagus with tissue from another part of the body, usually from the stomach or the skin on the forearm or thigh. The surgery may also involve a thoracic incision in the area of the primary tumor depending on where it is located.
The function of the esophagus is to transport bolus (liquid and solid foods) from the mouth, through the throat, into the stomach through peristalsis. The upper esophageal sphincter (UES), which is formed by circular bundles of muscle tissue, remains closed in a contracted position until swallowing occurs and the muscles relax temporarily. This allows the passage of the bolus into the esophageal body through primary and secondary peristalsis.
The cervical esophagus is innervated by parasympathetic nerves originating in the vagus nerve and spinal nerves from segments T1 to T10 via the thoracic sympathetic trunk. These nerves primarily control parasympathetic motor functions of the esophageal muscles and glands. They also serve to sense pressure in the esophagus, with the vagus nerve detecting pressure that can translate into pain and the thoracic chain more directly sensing pain. These nerves help to contract and relax the UES, LES and peristaltic movement of the esophagus. In addition, the thoracic and cervical chain nerves help to control the secretory activity of the esophagus. They also help to maintain a normal ph of the esophagus and regulate acid secretion.