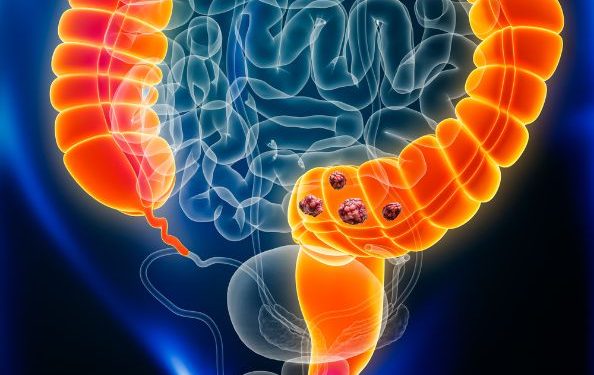
Duodenal cancer is rare, but it can be deadly if not diagnosed early. The duodenum is the first part of your small intestine that food enters after leaving the stomach. It helps your body absorb the nutrients from your foods. Doctors don’t know what causes duodenal cancer, but they think it starts when genes go awry and grow uncontrollably into tumors. Certain things may raise your chances of developing the disease, such as age (most duodenal cancers are found in people 60 to 80), health conditions like celiac disease and Crohn’s disease, smoking and drinking too much alcohol and eating a diet high in red meat, sugar and refined carbohydrates. Some genetic disorders, such as familial adenomatous polyposis and Lynch syndrome, also increase your chances of getting duodenal cancer.
It can be hard for doctors to diagnose duodenal cancer because its symptoms are so vague and similar to those of other illnesses. These include abdominal pain, weight loss, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, anemia and bleeding from the tumor. These symptoms can be caused by many other conditions, including irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease and tuberculosis of the intestine.
Diagnosing duodenal cancer requires a physical exam, medical history and an interview about your lifestyle, including any past health problems, family history of diseases and habits such as smoking and drinking. You may also undergo tests that include blood and imaging studies. Blood tests check your levels of certain chemicals that may be released by cancer cells. For example, levels of carcinoembryonic antigen, or CEA, rise when you have duodenal cancer. Imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) create pictures of your GI tract to help find the location of a tumor.
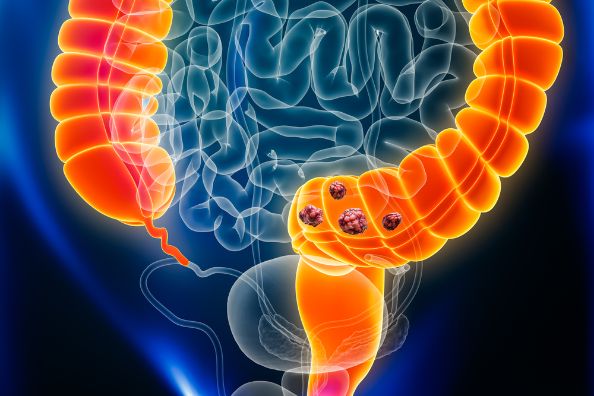
Treatment for duodenal cancer depends on how far the tumor has progressed. At stage 0, the cancer is in your duodenum only and hasn’t spread to surrounding tissue or lymph nodes. At stage 1, the cancer is in your duodenum and has spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes. At stage 3, the cancer has spread throughout your abdomen and at least one other organ such as the lungs or liver.
Some treatments may include chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Chemotherapy kills cancer cells and may shrink tumors. Radiation therapy targets the area with high-energy beams that can shrink or destroy cancerous tissue.
Some herbs and natural remedies can also relieve duodenal cancer symptoms. Talk to your doctor if you want to try using these herbal treatments. They can tell you which ones to avoid and how to safely use them. In some cases, they may suggest combining natural therapies with other treatments. This combination is called integrative medicine and may improve your outlook for survival. It can also reduce unpleasant side effects of some treatments, such as chemotherapy.