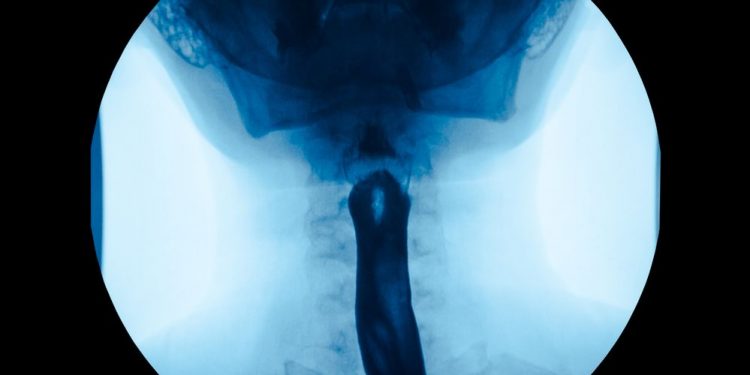
The most common symptom of esophageal cancer is a problem swallowing. This can feel like food is stuck in the throat or chest and may even cause choking. This problem gets worse as the cancer grows and narrows the opening of the esophagus. It usually occurs in people with squamous cell carcinoma. This type of esophageal cancer starts in the flat cells lining the esophagus, which are found in the upper and middle portions of the esophagus.
Other Symptoms
Esophageal cancer can also spread to the nearby lymph nodes and other tissues. This can cause other symptoms, such as chest pain or a feeling of pressure in the middle of the chest. It can also cause a lump or an abnormal area to form in the esophagus.
Occasionally, the tumor can also cause bleeding in the throat. This blood then makes its way into the stomach, where it can cause nausea and vomiting. This bleeding can also turn the stool black. Some people may also experience anemia, or low red blood cell counts, due to the blood loss.
Other Symptoms
Sometimes, the cancer can spread to other parts of the body, such as the bones, lungs or liver. This can cause other symptoms, such as a feeling of shortness of breath or chest pain, nerve paralysis, hoarseness or hiccups.
A doctor will ask about your medical history, including any of these symptoms. They will also look at you closely. You may have other tests, such as an X-ray or CT scan of your chest and abdomen.
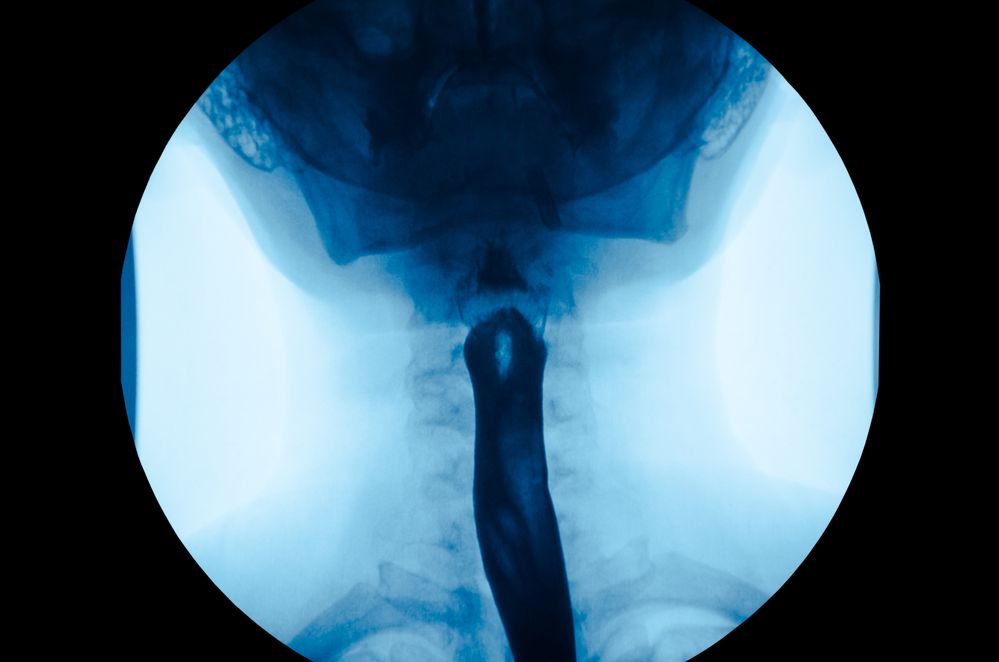
You may also be given a test called an endoscopy, which is a thin tube with a camera attached that lets the doctor examine your digestive tract. They may also remove a small amount of tissue (biopsy) to check for signs of cancer.
They may then send this sample to a laboratory where the tissue is examined for any signs of cancer. They may also give you a drug called an anti-neoplastic agent to help prevent the cancer from coming back.
These medicines are often combined with other treatments, such as radiation therapy or surgery. They can also be used alone to treat some types of esophageal cancer.
Managing your risk
The most important thing you can do to lower your risk of esophageal cancer is to stop smoking and to cut down on alcohol use. You should also eat a healthy diet, and exercise regularly to keep your weight down.
Your doctor can give you more information about esophageal cancer and its symptoms. He or she can also tell you if you are at risk of developing the disease.
Some symptoms of esophageal cancer are more likely to be caused by problems other than cancer, so they won’t always tell the doctor whether you have the disease or not. However, it’s still important to tell your doctor if you notice any of these symptoms so that they can be treated if needed.
If you have any of these symptoms, make an appointment with your doctor to get checked out. The doctor can also prescribe medications to relieve these symptoms if needed.