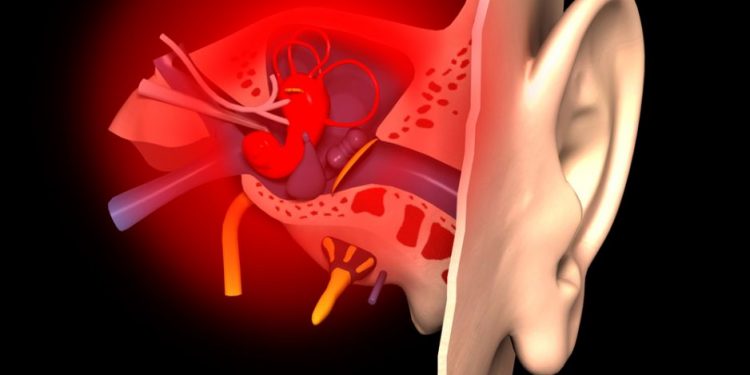
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD) is a condition that can cause serious problems for the individual. It can cause pain, pressure, swelling, and even a loss of hearing. This condition can be treated, but may take some time. If you suffer from ETD, make sure to seek treatment promptly.
Eustachian tubes are responsible for keeping air pressure in the middle ear from building up. When the tubes become congested, the fluid that helps prevent this pressure from building up becomes trapped. Symptoms of this condition include hearing your own voice loudly, having difficulty putting your ears underwater, and feeling like your ears aren’t popping. Other symptoms of eustachian tube dysfunction can include a loss of hearing in your upper or lower ear.
Eustachian tubes can be clogged for many reasons, including excess mucus, a tumor, or enlarged adenoids. In addition, some people with Eustachian Tube Dysfunction may have allergies that are worsening the condition. For these individuals, antihistamines, chewing gum, and chewing your tongue may be able to help relieve the symptoms.
The Eustachian tube is important for the middle ear because it allows air to flow into the ear and keeps it free from moisture. Because of this, it is necessary to clear the passageways of mucus, dirt, and other debris. Chewing your tongue, chewing on a stuffed ear, and swallowing can help to open the tube and remove the buildup of pressure. Using an irrigation system or saline nasal sprays can also help to clear the passageways.
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction is a common sinus problem, but it is not always easy to diagnose. The best way to determine whether you have this disorder is to discuss your symptoms with your healthcare provider. Symptoms of ETD can last for days or weeks, so it is important to see your doctor if they persist.
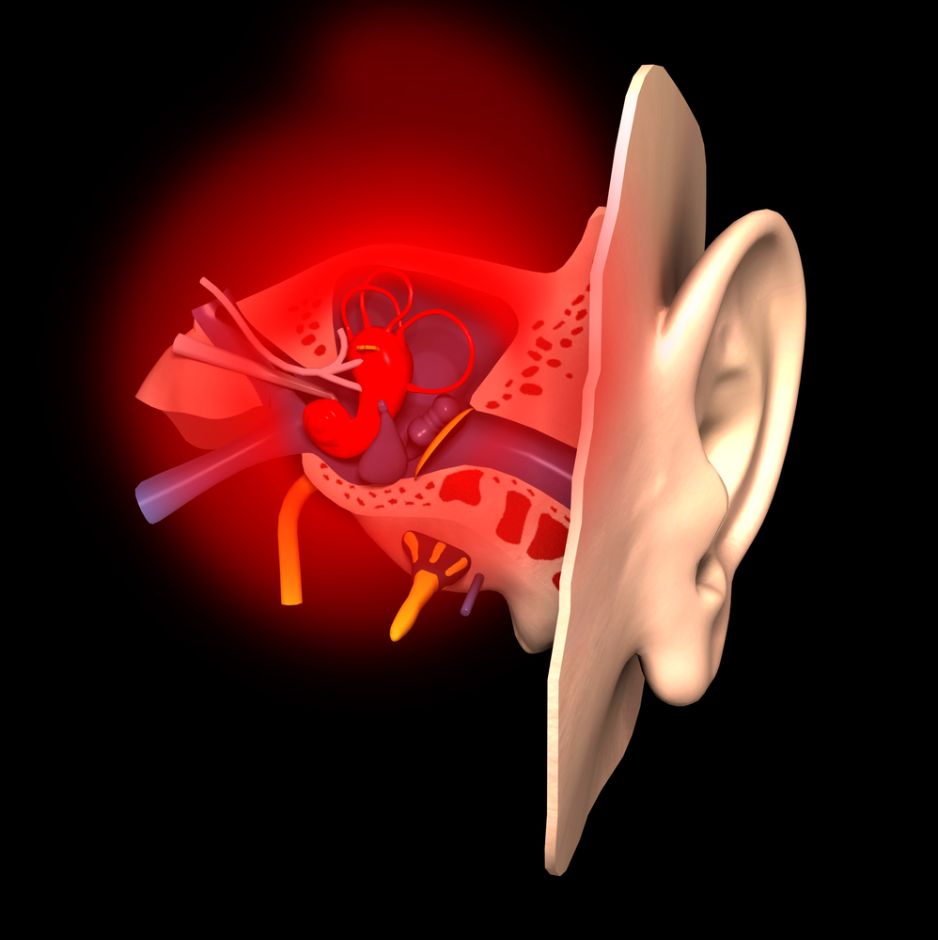
Children are more susceptible to Eustachian Tube Dysfunction than adults. These children’s eustachian tubes are smaller and more flexible, which makes it easier for germs to enter the ear. Typically, children develop ear infections after respiratory infections, which are usually caused by bacteria. A recurrent ear infection can also cause Eustachian Tube Dysfunction.
Usually, ETD does not cause damage to the eardrum, but it can be an indicator of other medical conditions. Your doctor can determine the causes of your symptoms and offer the right course of action for your particular situation. Depending on the severity of your condition, your doctor may prescribe medication, surgery, or other treatments.
You can find out if you have Eustachian Tube Dysfunction by undergoing a tympanogram. Tympanograms show the movement of the tympanic membrane as a series of spikes. If your tympanogram is abnormal, your physician may want to conduct an otoscope, which uses a small magnifying lens to examine the tympanic membrane. However, otomicroscopy can be more useful, as it can show tiny tympanic membrane movements.
You should seek treatment if your symptoms of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction last more than two weeks. Treatment may include prescription medications, saline nasal sprays, chewing gum, or over-the-counter medicines.