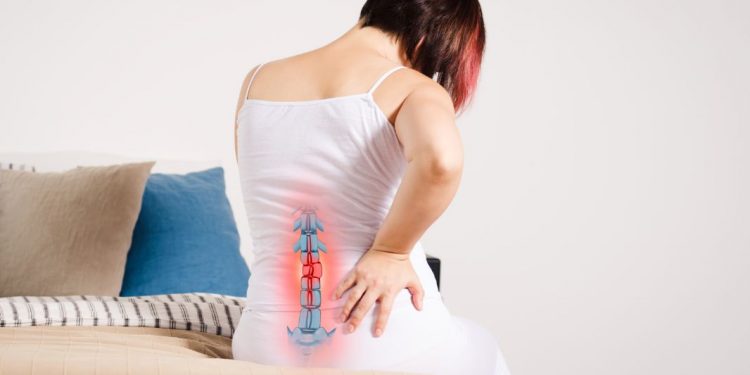
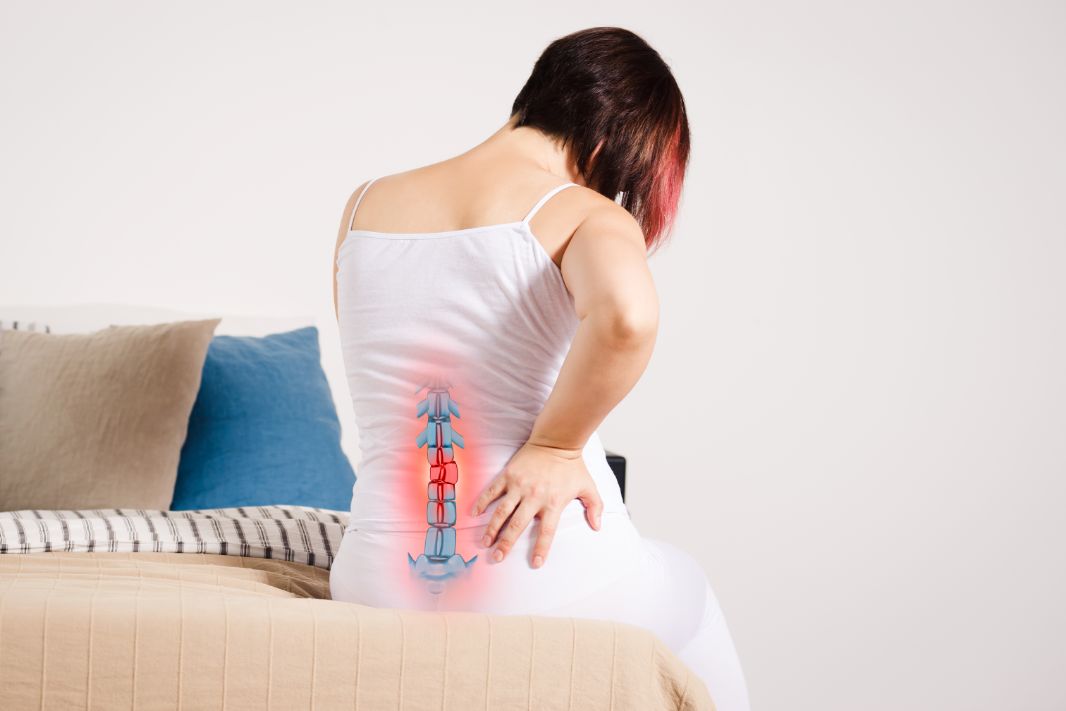
When you have herniated disc symptoms, it is important to understand your condition and find a treatment that will work for you. A herniated disc is a common spinal injury that can cause pain, numbness, and weakness in the back, legs, and feet. In most cases, the pain is mild and goes away in a few weeks. If the pain is severe, surgery may be necessary to remove the herniated disc and stabilize the spine.
Herniated discs are caused by a jelly-like substance in the middle of the disk pressing against the outer layer of the disc. This pressure can cause irritation of the nearby nerve root, resulting in the symptoms. While herniated discs are most common in the lower back, they can also occur in the thoracic and lumbar regions of the body. The causes vary from simple stress to trauma.
Herniated discs can be treated with non-surgical methods. These include medication, rest, and physical therapy. Physical therapy can help reduce the pain and improve the range of motion. Patients who do not respond to conservative measures should see a physician to rule out other conditions.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications can be helpful for mild to moderate symptoms. They should not be used for long periods of time as they can be harmful. Your doctor will be able to recommend a suitable NSAID, or analgesic. You can also apply heat or ice to the affected area, which will relax the muscles. During the first few days, you should avoid lifting anything heavy. You should change positions frequently. Depending on your doctor, you may be told to take a low-activity level, avoid bed rest, and perform simple leg exercises.
Surgery is a last resort. It can reverse the effects of herniation. For some people, though, herniated disc symptoms persist and lead to permanent disability. However, it is rare to have herniated discs at an early age. Those who are overweight, smokers, or who have a family history of herniated discs may be at higher risk.

Surgical options may include removal of the herniated disc and placement of a bone spur. These procedures are performed under X-ray guidance and may also involve pain management. Other options include epidural injections or lumbar traction.
The use of pain medications, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and physical therapy are common treatments for herniated discs. Some patients need supervised rehabilitation to help them recover. Ultimately, recovery is the goal. Most people who are symptom free after six weeks of conservative treatments are able to return to normal activity.
Before making a decision on whether or not to have surgery, it is important to consult with your physician. He or she will be able to provide you with a detailed plan for recovery. You should not be afraid to ask questions. Ask your doctor about your options and how to decrease your risk of recurrence.
Your doctor may prescribe medications to relieve your herniated disc symptoms. Often, these medications are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Taking NSAIDs is not recommended for everyone, but they are often prescribed for individuals who suffer from herniated discs. Long-term use can have negative effects on the liver and kidneys. Analgesics such as acetaminophen are also useful, but they should only be taken for a few days.