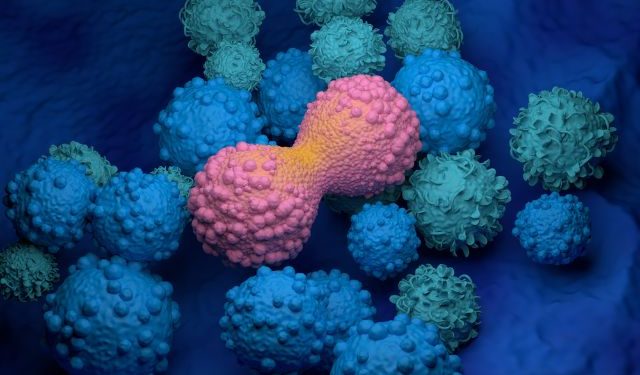
Non hodgkin’s lymphoma symptoms include swelling in the lymph nodes (lymphadenopathy), blood abnormalities, and sometimes skin problems. Some types of non hodgkin’s lymphoma can cause serious health problems if not treated right away.
Lymphomas are cancers of the immune system. The immune system is the body’s defense against viruses, bacteria, and other foreign substances. It also protects against diseases such as AIDS and some forms of leukemia. Non hodgkin’s lymphoma starts when lymphocytes, a type of white cell, develop abnormally and grow out of control. The cancer cells grow quickly and crowd out the normal cells, which can’t do their work.
There are many different kinds of non hodgkin’s lymphoma. Some grow and spread at a slower rate than others and have fewer signs and symptoms. The different kinds are grouped for treatment according to whether they’re indolent or aggressive and whether the lymph nodes with the cancer are contiguous or not.
B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. This group includes diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, and mantle cell lymphoma. B cells are a type of lymphocyte that fights infection by producing antibodies to neutralize foreign invaders. B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma can also spread to other parts of the body, including bone marrow, blood, and the spleen.
Plasmablastic lymphoma. This is an aggressive form of B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma that usually begins in the chest wall lining, in the sac around the lungs and heart (pleural effusion), or in the abdominal cavity. Plasmablastic lymphoma often occurs in people infected with HIV.
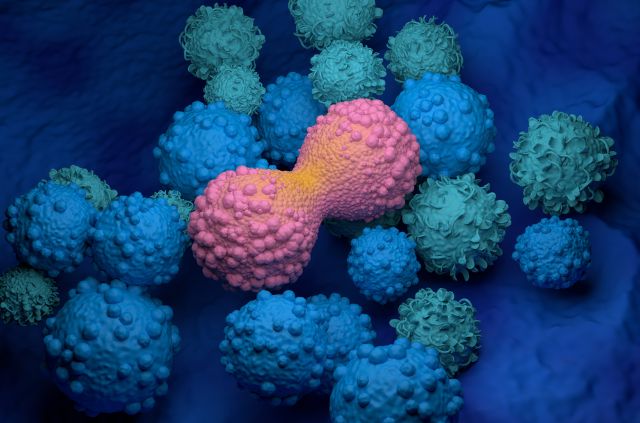
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma spreads to other parts of the body through the bloodstream. Some kinds of non hodgkin’s can also spread to the brain through the cerebrospinal fluid, or to other organs such as the liver or spleen.
Treatment for adult non hodgkin’s lymphoma may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a combination of both. Chemotherapy drugs kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. It can be taken by mouth or injected into a vein or muscle. It can also be put directly into the cerebrospinal fluid, an organ, or a body cavity such as the abdomen. It’s often given with steroid drugs, which lessen the side effects of the chemotherapy and help prevent organ damage.
Doctors don’t know what causes most cases of non hodgkin’s lymphoma. However, old age, being male, and having a weakened immune system increase your risk for this disease. Medications that suppress the immune system can also increase your risk. These medicines include some cancer treatments and some medications used to treat infections such as hepatitis and HIV infection. Certain viruses and bacteria can also increase your risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. These include the viruses HIV and Epstein-Barr virus, and the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Some people with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma have no known risk factors, but it can recur after treatment. For this reason, it’s important to see your doctor if you have any unusual or worrying signs and symptoms.