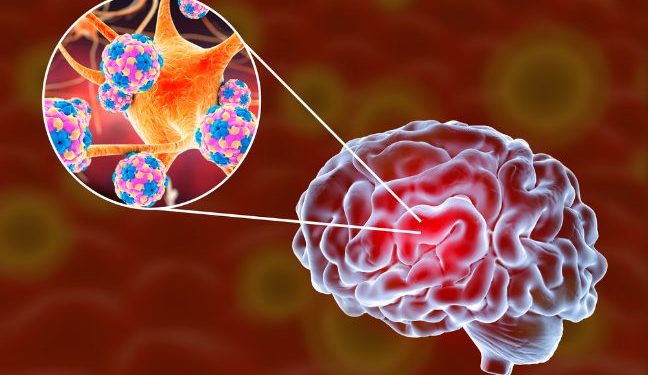
Japanese Encephalitis symptoms are a serious condition that is caused by the Japanese encephalitis virus. This viral infection is found throughout Asia and the western Pacific and can be a serious health risk to people who travel there or live in areas where mosquitoes are known to breed.
Symptoms typically begin about 4 to 15 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. A person may feel a fever or headache, throw up, or have stomach pain.
A doctor can diagnose Japanese encephalitis by looking at blood or spinal fluid. These tests can spot antibodies that your immune system makes to fight the disease.
There is a vaccine that prevents this disease, called Ixiaro. It is given in a series of two shots, 28 days apart. The vaccine is available to people aged 18 years and older.
This is the most effective way to prevent this disease. It is safe and effective, but you should get it at least 7 days before travelling to the area where the disease is most common.
If you do get this illness, the first thing your doctor will do is give you fluids through an IV and help you breathe so you can stay comfortable. Your doctor can also provide pain medicine, if needed.
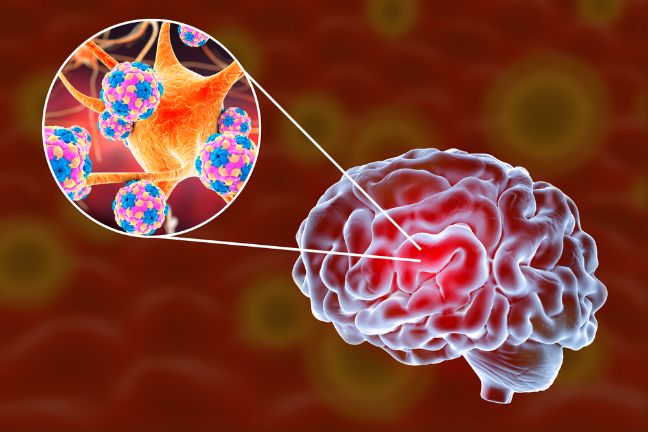
You might need to spend a day or more in hospital because of this severe condition, but rest and fluids can help ease your symptoms. The condition usually lasts a few weeks, but it can be life-threatening for some people.
It is important to know that this is a rare disease, and only 1% of people who have it develop symptoms. This is because it takes a very long time for the disease to inflame the brain and cause the symptoms that you may notice.
The most likely risk of getting Japanese encephalitis is from mosquito bites. Mosquitoes carry the virus in their saliva when they bite pigs and other animals.
However, mosquitoes can also catch this disease from humans. These include people who work in agriculture and those who do outside activities (e.g., camping, fishing) in areas where the water is flooded and where mosquitoes are active during the night.
Infected mosquitoes can be found in many areas, including rural and urban settings. They feed between sunset and sunrise, usually in ponds or marshes, where the animals or birds that they are feeding on have been infected with the virus.
JE is not a fatal disease, but it can be very debilitating and can cause permanent damage to the nervous system. About 20% to 30% of those who are ill with JE will develop lasting problems, such as seizures or paralysis.
This type of encephalitis can occur at any age, but it most commonly affects children. It can also occur in adults who have not previously been infected, particularly when traveling to countries where the disease is more common.
There are several ways to prevent the disease, including staying indoors at dawn and dusk and using insect repellent. It is recommended that anyone who is going to high-risk regions get a series of two shots of this vaccine, at least 7 days apart.