A doctor may use a variety of different diagnostic tests to diagnose liver cancer. One of the most common is a biopsy, which involves taking a small sample of liver tissue and examining it for signs of cancer. A CT scan, MRI, or ultrasound will guide the physician in the biopsy procedure. Other tests may include a laparoscopy, which is performed under a general anaesthetic. A laparoscopy allows your doctor to look inside your abdomen and take samples of the tissue. Liver cancer therapies are based on the type of cancer and its stage. They may also depend on the functioning of your liver.
Other symptoms of liver cancer include shortness of breath. The liver produces bilirubin, a yellow pigment that results from the breakdown of red blood cells. Bilirubin is a product of a malfunctioning liver and can cause an itchy skin. Although bilirubin doesn’t necessarily indicate liver cancer, it is an early warning sign of other health conditions. Therefore, it’s important to seek medical attention if you’ve noticed any of these symptoms.
Surgery to remove the affected liver tissue is another treatment option for patients with advanced liver cancer. A surgeon will remove the cancerous tissue along with a margin of healthy tissue. This procedure is known as partial hepatectomy, and the size of the cancer determines the extent of the surgery. There are several different types of resection for liver cancer, depending on the stage of the disease and the size of the tumor. However, it is best to discuss the option of surgery with your doctor before proceeding.
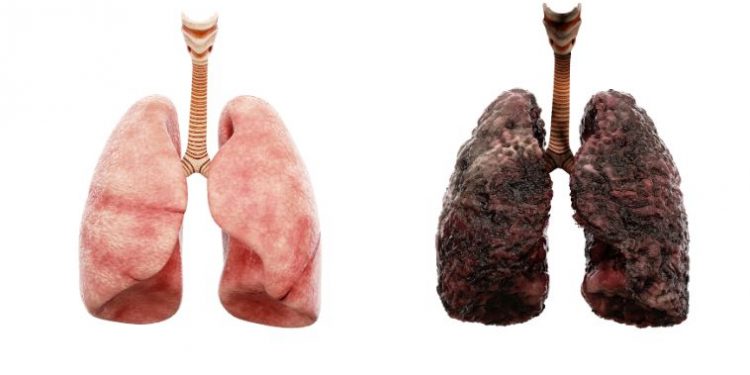
In general, the symptoms of liver cancer can vary from person to person. Because symptoms differ so much, it is important to seek medical care as early as possible. Early detection of liver cancer will improve the chance of a cure and a better quality of life. The best way to ensure this is to discuss the symptoms with your doctor and family. For most cases, liver cancer treatments consist of a combination of surgery and other therapies, which will usually be combined with a doctor’s orders.
Primary liver cancer is known as hepatocellular carcinoma. Other types of liver cancer are called bile duct cancer, or cholangiocarcinoma. The bile ducts are small tube-like structures in the liver that carry bile from the liver to the gallbladder. These ducts are the primary source of bile, and 85 percent of all cases are of this type.
Infections with hepatitis B are common in people of Asian or sub-Saharan Africa. Liver cancer may develop as a result of a cirrhosis condition where scar tissue builds up in the liver. People with diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease may also develop this condition. Exposure to aflatoxins (poisons produced by molds) in our food can increase the risk of liver cancer.

When liver cancer spreads from the colon or rectum, it’s called metastatic cancer. It starts in another organ and spreads throughout the body, including the liver. In fact, metastatic colon cancer is a type of primary liver cancer. It has the same symptoms as primary liver cancer, but the only difference is that the cancer has spread to the liver. In both types, the cancer cells have metastasized from the colon or rectum.
Chronic hepatitis is one of the main causes of liver cancer. People with a weakened immune system are five times more likely to develop it. People who are obese are at an increased risk of developing fatty liver disease, and it’s also important to note that the disease is more common in males than in females. Smoking also increases the risk of liver cancer. People who smoke are more likely to develop cirrhosis than those who do not smoke.
Patients diagnosed with liver cancer should try to stop smoking and reduce alcohol intake. If these steps are not possible, healthcare providers can recommend services and programs that can help people stop drinking. Besides quitting smoking and reducing alcohol intake, cancer patients should eat a nutritious diet and exercise regularly. While eating healthy may be difficult for some people with liver cancer, a dietitian can help you choose foods that provide nutrition and exercise.
Advanced stages of liver cancer can also cause fever and nausea. Patients may experience general weakness, mental confusion, and fatigue. The enlarged liver may cause pain in the abdomen and back below the right shoulder blade. Additionally, skin lesions may form. If liver cancer is detected early enough, the treatment may involve a liver transplant. However, it is important to note that liver cancer surgery may involve two different surgical procedures. A partial hepatectomy removes part of the liver and replaces it with healthy liver tissue.