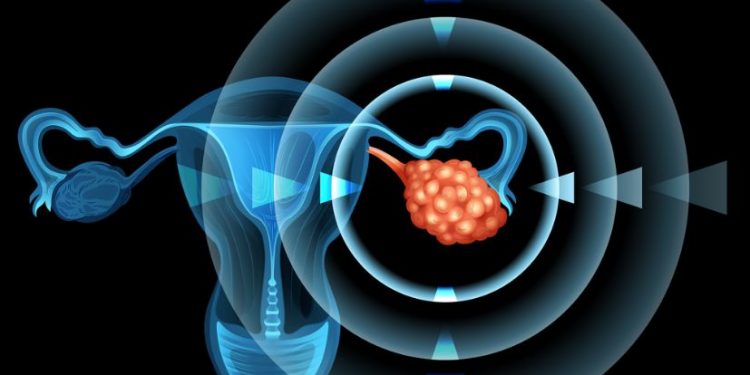
Ovarian cancer symptoms can be confusing. They may be associated with other health problems, or they may be signs of cancer that has spread to other organs. When these symptoms occur, a woman should see her doctor immediately. Symptoms are usually persistent and difficult to pinpoint.
The most common symptom of ovarian cancer is abdominal pain, but symptoms can also be related to liver disease, infections, and benign tumors. If you are experiencing unexplained abdominal pain, consult a healthcare provider. A urinalysis can help diagnose the cause of the abdominal pain. You can also request a pelvic MRI if you have questions about the location or status of the mass.
Other early symptoms of ovarian cancer include bloating and abdominal swelling. The tumor may also cause urinary symptoms such as an increase in the urge to urinate. As the tumor grows, it may block the bladder and compress the bladder, causing lower abdominal pain and bloating.
Women who experience these symptoms should be screened for ovarian cancer. They are more likely to have a recurrence of the disease once it is diagnosed. Some women are able to respond to basic treatment, while others may have to undergo more aggressive therapy. During the initial diagnosis, the pathologist will evaluate tissue samples to determine if the cancer has progressed. In addition, the surgeon may remove as much of the tumor as possible.
Those with ovarian cancer are at a high risk for recurrence. This is because the tumors can grow back after initial treatments. It is important to be treated as soon as possible, because the cancer is prone to spreading. Surgery is the main treatment for ovarian cancer. After surgery, the surgeon may need to remove the ovaries.
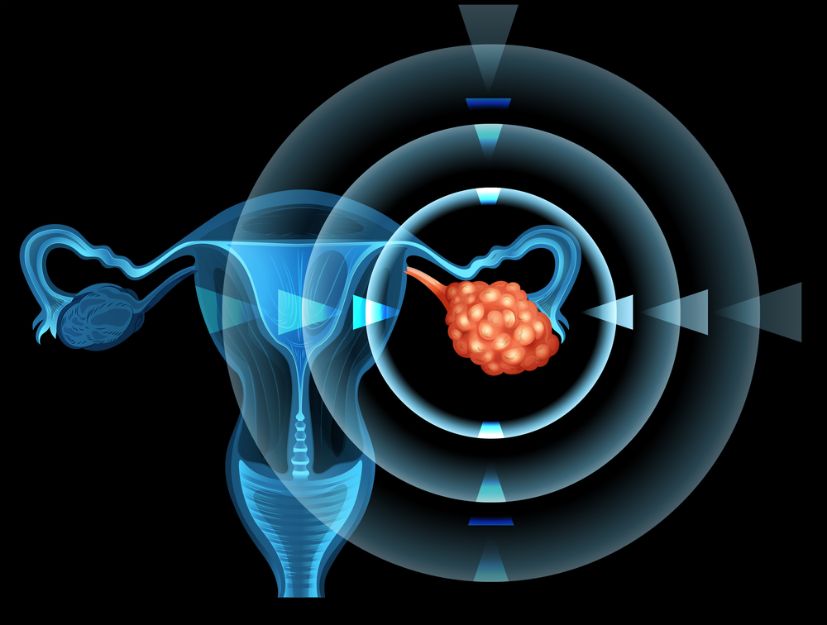
Ovarian cancer often goes undiagnosed until it is more advanced. Fortunately, new treatments have improved the outlook for patients. These treatments can attack the cancer cells and do little damage to the normal cells in the body.
Depending on the stage of the disease, the doctor may perform imaging studies to find the location of the lump and determine if it has been growing for a while. Imaging studies can also help the pathologist confirm the diagnosis. Often, the size and composition of the lump can be determined through ultrasound. During the procedure, a pathologist may use diagnostic immunohistochemistry to identify whether the tumor contains definite signs of cancer.
Other symptoms of ovarian cancer can include abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, back pain, and fluid accumulation in the pelvis. Generally, symptoms are more severe in advanced stages of the disease. However, they can also appear in the early stages of the disease, even if the tumor has not yet grown.
Ovarian cancer is an extremely serious disease that affects a large number of people. Approximately 20 percent of cases are diagnosed in the early stages. Most people are diagnosed with the disease in its advanced stages. Although there is no specific screening test, a woman’s age, family history, and menstruation are risk factors for developing the disease.