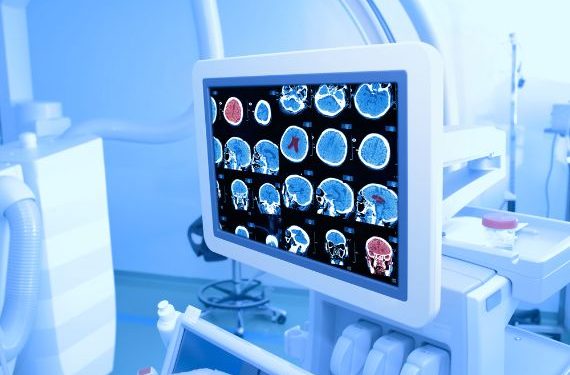
But there are cases when a tumor can spread to the heart, and these can lead to life-threatening complications. To learn more about the risks and treatment options for cancer near the heart, read on. Below is an overview of the three most common types of cancer near the heart. A tumor in the heart is usually the result of a genetic malformation.
A primary cardiac tumor is an extremely rare condition, but it can be deadly for young people, especially if it has spread from other organs. Early detection and aggressive treatment are essential for this type of cancer, which is why early surgical intervention is recommended. Fortunately, there are many treatments for cancer near the heart, including systemic chemotherapy. If you suspect you may be suffering from a heart tumor, don’t hesitate to schedule a consultation with a physician at a specialist center.
There are two types of cancer near the heart: benign and malignant. Benign cardiac tumours, or those that do not spread to other organs, are less common. However, they can still grow large and block part of the heart. They can also affect the structure of the heart, making it difficult to remove. The most common benign heart tumour is atrial myxoma, while others include lipomas and fibromas. Both types of heart tumors can be life-threatening if left untreated.
A primary heart tumour may develop in the tissue surrounding the heart. It can affect the heart muscle, valves, and the pericardium, resulting in abnormal heart rhythms, abnormal heart function, and even a stroke. It can also squeeze the heart muscle, preventing the heart from filling with blood. Ultimately, it can lead to heart failure. If left untreated, this condition may cause a patient to suffer a wide range of symptoms, including chest pain, shortness of breath, and dizziness.
Surgical treatment for cancer near the heart is available for patients who are suffering from a heart attack or stroke. However, surgery can be complicated and time-consuming. A surgical procedure involving open heart surgery can only be performed if the tumor is small and the tumor is within the heart. The heart is an extremely sensitive organ, and the surgeons must carefully cut the heart’s vital network while removing the tumor. This process is often complicated and painful, and the chances of a successful recovery are high. The survival rate of a patient undergoing cardiac surgery is a little over a quarter of the population.
Surgery for a tumor near the heart can be performed in a number of ways. It can be performed with local or general anesthesia. The surgeon will use a thin, flexible tube to insert it into the chest. This tube will then be attached to a special bottle and drain fluid from the body on a regular basis. If it is cancer near the heart, the tumor may have spread to other parts of the body, which can cause shortness of breath or pneumonia. Treatment for this type of cancer will typically include radiation therapy or other techniques to relieve the blockage.