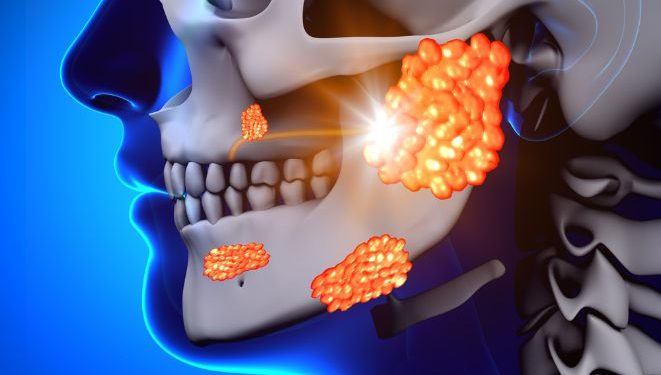
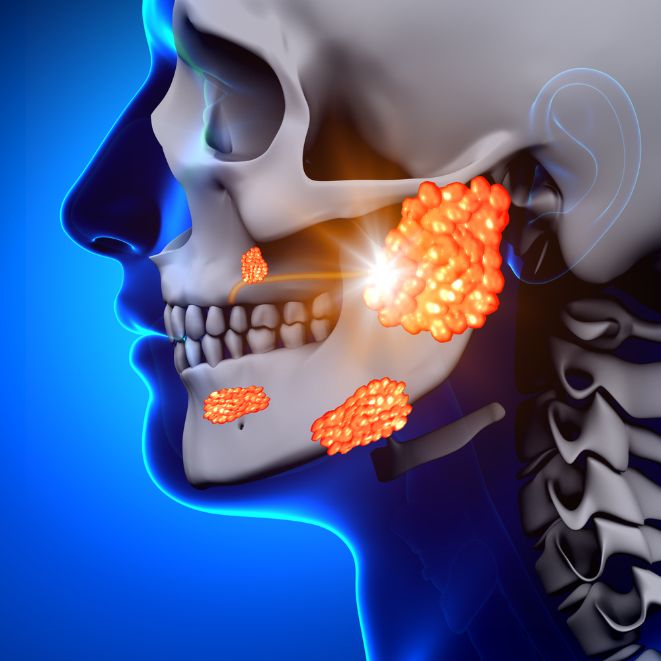
Mumps is a viral infection that usually affects the salivary glands, particularly those in the parotid glands on each side of the face. It used to be common in children, but thanks to the mumps vaccine (MMR) most people don’t get it anymore.
Symptoms of mumps develop within a few days after a person has been exposed to the virus. Some symptoms are mild or don’t occur, and some may be very serious.
A fever of 103 F (39 C) or higher is a common symptom of mumps. Swelling of the glands in the cheeks and jaw is also a common symptom. The swollen glands can be tender and painful.
Other signs and symptoms include headaches, joint pain, a high temperature, swollen lymph nodes in the neck and a sore throat. In some cases, the infection can spread to the brain or spinal cord and cause viral meningitis.
The mumps virus can be spread through droplets of saliva that are released when an infected person coughs or sneezes. It can also be passed through contact with objects that have been touched by someone who is infected. These include spoons, utensils and cups that have come into contact with the saliva or mucus of an infected person.
Swelling of the parotid glands in the cheeks and jaw is the most recognisable symptom of mumps. This swelling gives a person a “hamster face” appearance and can cause pain and tenderness.
It’s important to see a doctor for an accurate diagnosis as soon as possible. Your doctor will listen to your throat, take a sample of your saliva or do a test called a throat culture. They will probably also do a blood or urine test.
Most kids are protected from mumps with the MMR and MMRV vaccines. These are given at 12-15 months and again at 4-6 years old. They help to prevent mumps in 80-90 per cent of kids.
If you’re a child, it’s important to stay home from school and childcare while you have mumps. You’re still contagious even before the facial swelling starts, so it’s best to stay at home until your doctor says you can no longer pass the mumps virus onto other people.
It is also recommended to avoid contact with others until at least 5 days after your symptoms start. The mumps virus is very contagious for about 9 days after your glands start to swell.
During this time, you should avoid wearing tight clothing, including socks and shoes. You can use cold compresses and rest to help relieve your symptoms.
Mumps is a very contagious virus that can be spread easily from one person to another through coughing, sneezing or talking. It can also be spread by eating food or drinking liquids from someone who is infected.
When you’re sick with mumps, it is a good idea to avoid sharing food or drinks with others and to eat mushy foods that are easy to chew. This will ease the pain and discomfort of your swollen glands.