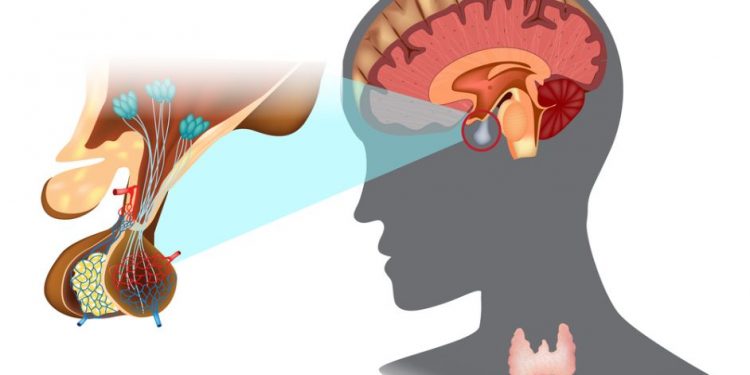
The symptoms of neuroendocrine tumors vary depending on the type of tumor and its location. For example, a patient with a pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor may experience diarrhea and weight loss. In contrast, a pheochromocytoma patient may suffer from rapid fatigue and tachycardia. Symptoms will also depend on the size of the tumor and whether it has become cancerous.
Neuroendocrine tumors are usually located in the pancreas, thyroid, or adrenal glands. They can also develop in other parts of the body. Symptoms can include edema, hypertension, and high blood sugar.
Endocrine tumors are often treated with surgery and radiation therapy. During surgery, the tumor can be removed and a tissue sample taken to be examined by a pathologist. The tissue sample can be used to determine if the tumor contains cancer cells. A tumor that has spread may need to be treated with chemotherapy or targeted regimens. However, many patients with these tumours are treated successfully and have long periods of good health and well-controlled symptoms.
Patients with endocrine tumors are treated by a multidisciplinary team of doctors. They meet weekly to discuss treatment options for each patient. Treatment can involve hormone therapy, peptide receptor radionuclide therapy, surgery, and drug therapy. Somatostatin analogues can also be given to help control the disease.
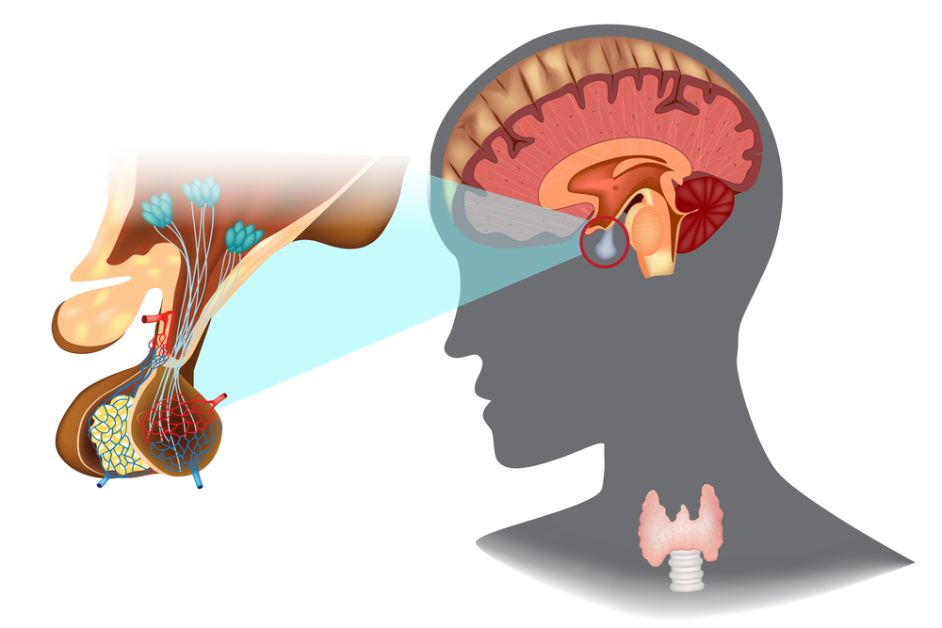
A neuroendocrine tumor can produce excess hormones that can affect the organs where the cells are located. For instance, a pheochromocytoma can cause tachycardia and adrenergic symptoms, such as hypertension. If the tumor is cancerous, it can destroy the pancreas and other organs, causing symptoms like muscle weakness.
The symptoms of neuroendocrine tumors are varied, and the diagnosis can be difficult. Many patients have a marfan-like appearance or scoliosis, as well as other skeletal manifestations. Some have hyperparathyroidism, a condition caused by a malfunctioning parathyroid gland. When an endocrine tumor affects the thyroid, the symptoms can include a lump in the neck, a swollen thyroid, and an overactive thyroid. Depending on the type of endocrine tumor, treatments can include radiation or chemotherapy, or both.
Unlike other types of cancer, endocrine tumors don’t usually have a clear cause. Doctors can’t tell if the cause of the tumor is the tumor itself, an infection, or another medical condition. Because these types of tumors can be slow-growing, they may not cause noticeable symptoms until they are advanced. Nevertheless, they can still impact the patient’s quality of life.
Neuroendocrine tumors can affect any area of the body, but they are most commonly found on the skin. They can be flesh-coloured or pink and may appear as a hard nodule. People who have these types of tumors have an average age of fifty to sixty.
Although these tumors are a rare disorder, they can cause significant symptoms. Some symptoms include: low potassium levels, muscle weakness, high blood pressure, and diarrhea. Other symptoms can include: nausea, vomiting, high blood sugar, and gallstones. To prevent these complications, it’s important to follow doctor’s instructions and eat healthy foods and get plenty of exercise. Also, seek advice from your doctor if you’re unsure about what you should be eating or doing.