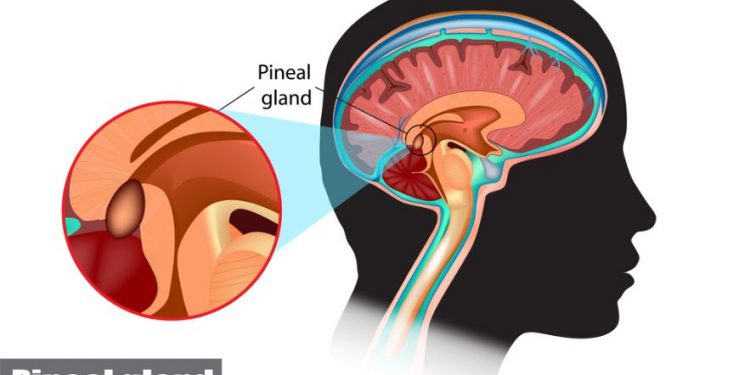
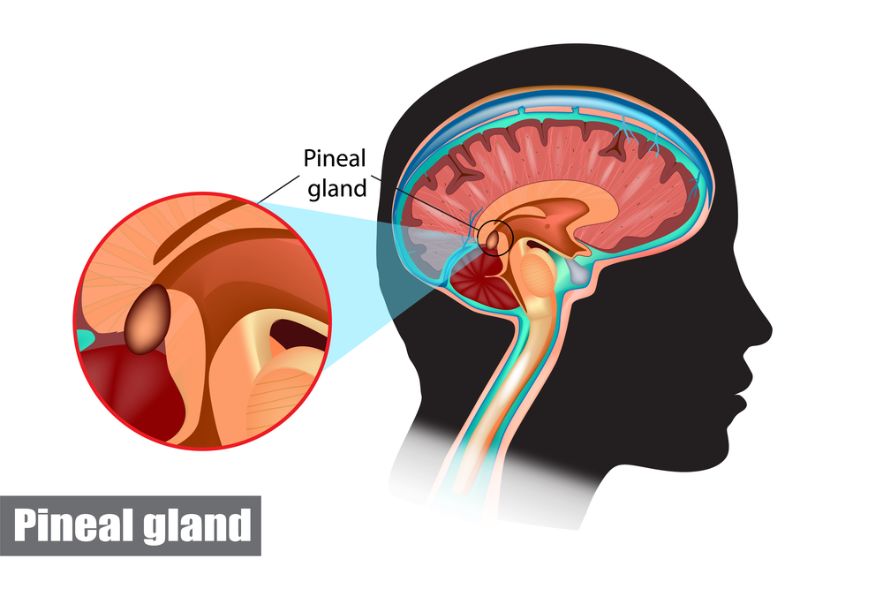
Neuroendocrine tumors are cancerous conditions that develop in the body’s neuroendocrine system. They can occur anywhere in the body, including the gastrointestinal tract, the lungs, and the pancreas. The symptoms of neuroendocrine tumors vary, and they can be quite aggressive. Some symptoms include weight loss, a feeling of bloating, and diarrhea.
When you are diagnosed with a neuroendocrine tumor, you will receive a number of tests to check for the tumor and other factors. You will also need a biopsy of the tumor, which is an invasive procedure. This involves taking a small tissue sample, which is then examined under a microscope. Your doctor may also test for genetic conditions that are associated with your tumor.
If you have a neuroendocrine tumor, you should seek medical care as soon as possible. The condition is rare, but can cause a variety of symptoms. However, the symptoms you experience will depend on where the tumor is located and what type of hormones it produces. In some cases, you may not experience any symptoms.
Symptoms of neuroendocrine tumors usually don’t appear until the tumor has spread. A person with a tumor that produces more than enough hormones will have a higher risk of experiencing symptoms. For example, if the tumor is producing too much insulin, you might have symptoms such as excessive thirst and urination. Other symptoms are similar to those of diabetes, and may include fainting, fatigue, dizziness, and increased appetite.
X-rays, blood and urine tests, and CT scans are common ways to diagnose a neuroendocrine tumor. During your examination, your healthcare provider will ask you about your family history and perform a physical exam. He or she will then recommend other types of tests.
Depending on the size and location of your tumor, you might undergo surgery. Surgery might be combined with other forms of treatment, such as chemotherapy, targeted radiation, or immunosuppression. Most drugs target the growth of the tumor and the production of its hormones. Treatment varies depending on the type of tumor, its stage of development, and your overall health.
In some cases, neuroendocrine tumors can be treated with immune system therapies. These treatments are effective, but may require additional treatment. Before undergoing any treatment, you should contact a physician at Baptist Health to discuss your options.
While neuroendocrine tumors are relatively uncommon, they can be life-threatening. They can occur anywhere in the body, and they can also spread to other areas of the body. It is important to consult with a physician at Baptist Health if you are experiencing any symptoms of neuroendocrine cancer.
Neuroendocrine tumors are caused by changes in the DNA of the neuroendocrine cells. These changes tell the cells to multiply and form a tumor. Neuroendocrine cells are found throughout the body, including in the intestines, appendix, lungs, and pancreas. The exact cause of the disease is unknown, but related genetic conditions are believed to contribute to the development of a neuroendocrine tumor.
Symptoms of neuroendocrine cancers may vary according to where the cancer is located and how much the tumor is growing. The symptoms are most common in the gastrointestinal system.