Pneumonia symptoms are a symptom of an infection in your lungs, caused by germs that can be inhaled into the air. The germs cause inflammation of the lungs’ air sacs (alveoli), and they fill up with fluid and pus. These fluids block the airways, making it harder to breathe.
The CDC notes that pneumonia can be spread from person to person by sneezing, coughing or touching surfaces that have been contaminated with mucus from an infected person. It can also be caused by bacteria or viruses from the common cold and other respiratory illnesses, such as influenza and adenovirus.
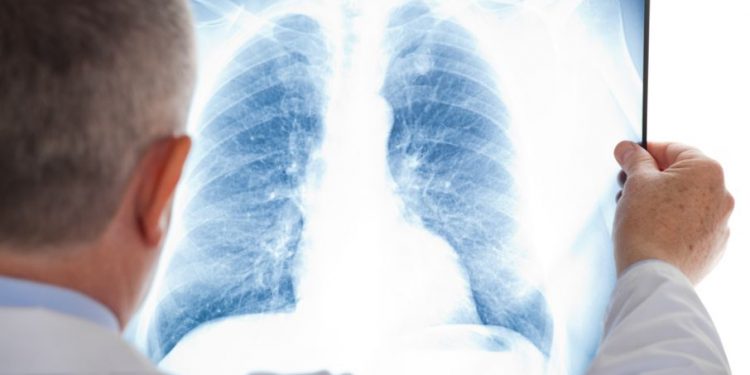
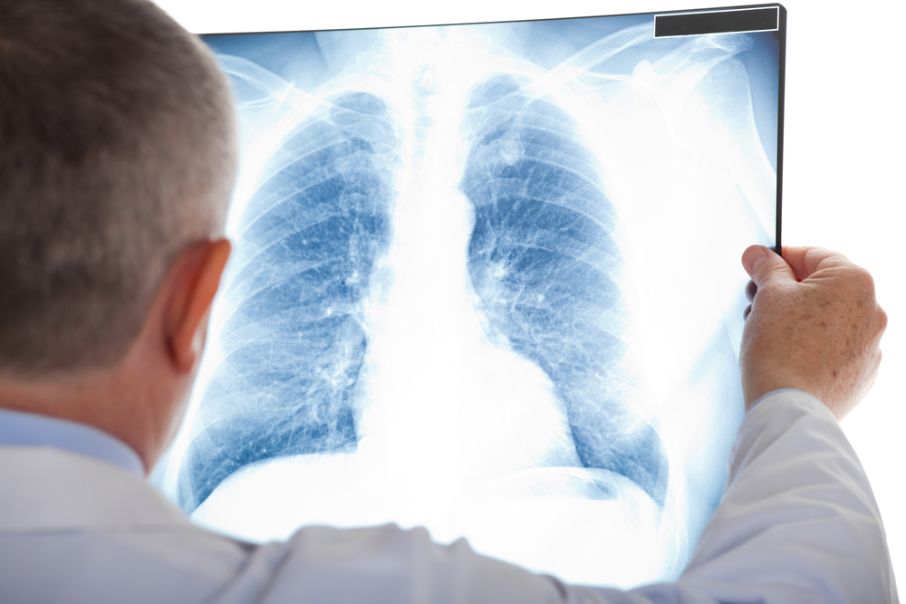
If you think you may have pneumonia, see a doctor right away. They can check for other conditions that might be causing your symptoms and perform tests, including a chest X-ray and blood and sputum test.
They can give you an antibiotic to fight the germs that are causing your pneumonia. The type of antibiotic that your doctor gives you depends on the bacteria that are causing your pneumonia.
Antibiotics are a quick and effective way to treat pneumonia. They work against both bacteria and viruses.
The most common symptoms of pneumonia are chest pain, difficulty breathing, a high fever and a cough with mucus that is yellow or white in color. You should call your doctor if these symptoms are severe or if they don’t get better within 48 hours of starting treatment.
People who are more at risk for developing complications of pneumonia include those with a weakened immune system or chronic health problems such as heart disease or diabetes. They may need to be hospitalized for care.
Getting treated in the hospital can help you recover more quickly and prevent pneumonia from returning in the future. Your doctor can give you antibiotics, fluids through a vein, and oxygen to help you breathe more easily.
Your doctor might want to do a chest X-ray or other test to check for other things that could be causing your pneumonia, such as lung abscesses. Your doctor might also order a pulse oximetry test to check how well your lungs are moving oxygen into your bloodstream.
Other symptoms of pneumonia are a lower-than-normal body temperature, confusion, and a headache. These symptoms can signal a more serious illness, such as a stroke. They also can indicate that you have a serious health problem, such as sepsis.
The most serious complication of pneumonia is bacterial infection in your bloodstream called bacteremia, or sepsis. This can lead to dangerously low blood pressure and septic shock, or organ failure.
It’s also possible to have a fluid buildup around your lungs (pleural effusion). This can make it hard to breathe and can lead to death if left untreated. You might need a chest tube to drain the fluid or surgery to remove it.
Usually, you can recover from pneumonia by taking medication and drinking plenty of fluids. Getting rest and doing breathing exercises can also help your body fight off the germs that are causing the infection.