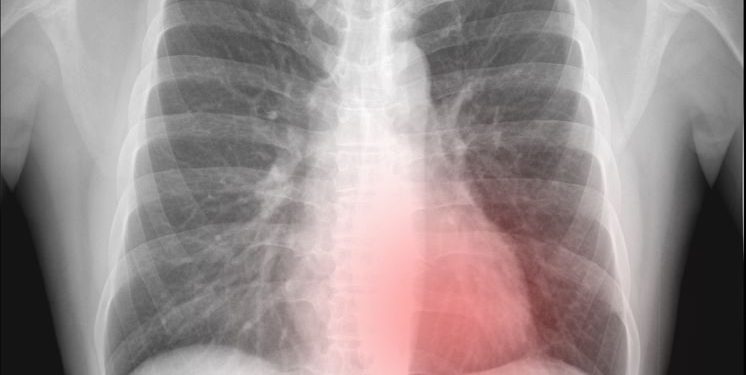
Depending on the amount of air that is trapped in the chest, a person with a pneumothorax may suffer shortness of breath, chest pain, or bluish skin. These symptoms can be life threatening and should be treated immediately.
Pneumothorax can occur when air leaks from the lung into the pleural space, which is the space between the lungs and the chest wall. This can be caused by an injury to the lung, such as a gunshot wound, or a medical procedure, such as a surgery. It can also occur as a result of a condition in the lungs, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or asthma. Other causes include smoking or a disease that damages the pleura, which is the layer of smooth tissue that lines the chest.
In most cases, the air will be absorbed by the body over a period of time. If the air is trapped, it can exert pressure on the lungs, which will eventually cause them to collapse.
When a person has a small pneumothorax, the air will probably go away on its own. However, it may take several days before a person realizes that something is wrong. It can also be difficult to diagnose. Most doctors diagnose pneumothorax using a chest X-ray. They also listen to the person’s breathing through a stethoscope. In other cases, a doctor may use a special light probe to look inside the person’s chest for an air leak. This is faster than using an X-ray and can be less painful for the patient.
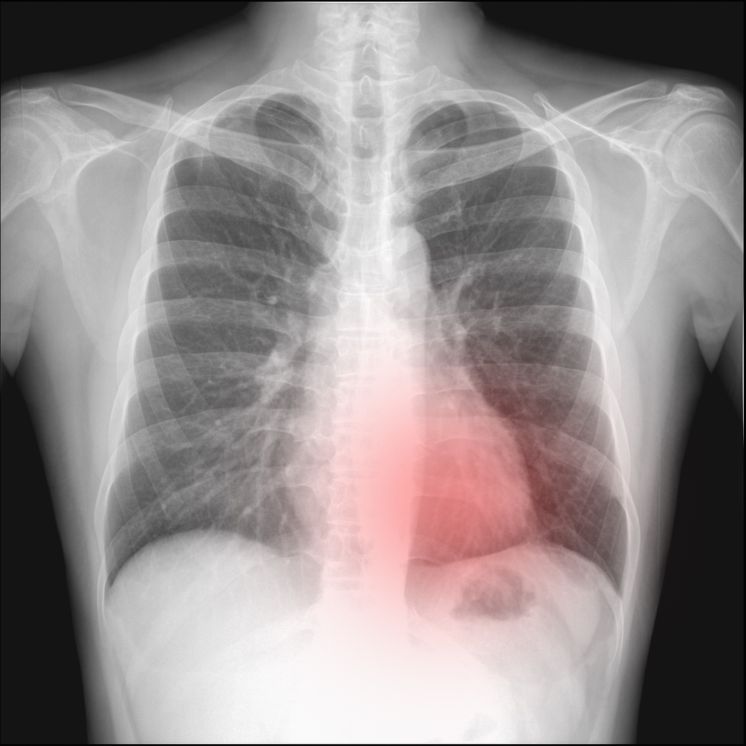
In the case of a traumatic pneumothorax, an injury to the chest wall or ribs causes air to leak into the pleural space. This can happen during physical assaults or medical procedures, such as a scuba diving trip. Symptoms may include shortness of breath, coughing, and chest pain.
In addition to these common symptoms, some patients may experience low blood pressure and fatigue. They may also experience a rapid heartbeat. Other symptoms may include distended neck veins and nasal flaring. In severe cases, patients may need to have a bronchoscopy or lung biopsy.
If a person experiences an emergency, they should be transported to a hospital in an ambulance. The person may also need to be given oxygen. They may also need to undergo a chest tube. The amount of treatment they receive will vary based on the severity of the pneumothorax. This may include surgery, as well as drugs to numb the pain.
Patients who experience severe symptoms of pneumothorax should be taken to a hospital immediately. They should also be given an arterial blood gas test to see if they have low oxygen in their blood. This test can also help diagnose tension pneumothorax, a severe form of the condition that can cause fast-paced, life-threatening symptoms. If a patient is hemodynamically unstable, they may need to have a needle decompression, which involves using a thin needle to release the air and allow the lung to expand more fully.