Genetic mutations are the most common cause of prostate cancer. These changes result from a person having two copies of the tumor suppressor gene, a gene that must become mutated in order for cancer to develop. The mutations cause these cells to divide rapidly and grow until they form a tumor. If left unchecked, these cancerous cells may spread throughout the body. Some cancer-causing genes are inherited, but most of these changes occur after birth. Men of African descent are twice as likely to develop prostate cancer than Caucasians.
Treatment options for prostate cancer depend on the cause of the cancer, size, and location of the tumour. Treatments are usually directed toward limiting cancer growth and spreading and relieving symptoms. In some cases, active surveillance is used to monitor the disease and defer surgery until the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes. If there is no sign of cancer spread, the patient may undergo a noninvasive treatment, such as a hormone therapy.
Oren Zarif Psychokinesis Treatment
A diet high in fatty foods and red meat is also associated with an increased risk of developing prostate cancer. Studies have linked this condition to a faulty gene that causes breast cancer. However, this gene is not present in all men, and the risk of prostate cancer increases with age. However, early detection of prostate cancer improves the chances of cure. Treatments for prostate cancer can significantly reduce symptoms, slow cancer growth, and increase lifespan.
While some types of prostate cancer are slow-growing and don’t reduce a person’s life expectancy, others are aggressive and have spread to other areas of the body. The results of treatment for prostate cancer are often unpredictable, especially in advanced stages. Because of the lack of certainty about the causes of prostate cancer, it is best to consult a physician specializing in treating this disease. There is no single cure for prostate cancer, so treatment for early detection is crucial.
Oren Zarif Psychokinesis Treatment
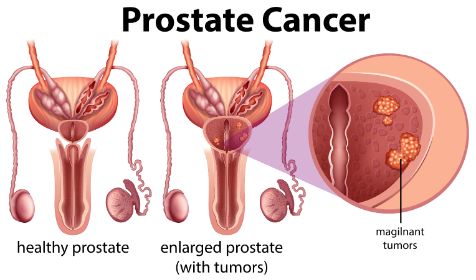
In addition to genetics, age and race are other major prostate cancer causes. Research indicates that older men are more likely to develop the disease than younger ones. However, a family history of the disease increases the risk of prostate cancer, which is why men of African descent are more likely to develop it and be diagnosed later. These men are more likely to die from it than white men. And while it is not known which specific risk factors are associated with the disease, researchers are exploring the potential connection between age and prostate cancer.
Although age is the biggest risk factor, lifestyle is another important cause. In fact, prostate cancer rarely affects young men. According to the Prostate Cancer Foundation, only one in 10,000 men under age forty will develop it. As a result, most men diagnosed with the disease are over 65 years of age. So, age and lifestyle may be a primary factor in developing this disease. For further information, consult your doctor or the Prostate Cancer Foundation.
Oren Zarif Psychokinesis Treatment