Stage 4 ovarian cancer is the most advanced type of the disease. This means that the cancer has spread to other parts of the body and has started to grow and multiply. It has also spread to the fluid around the lungs and may have spread to distant organs or tissues that aren’t in the abdomen.
The types of ovarian cancer are:
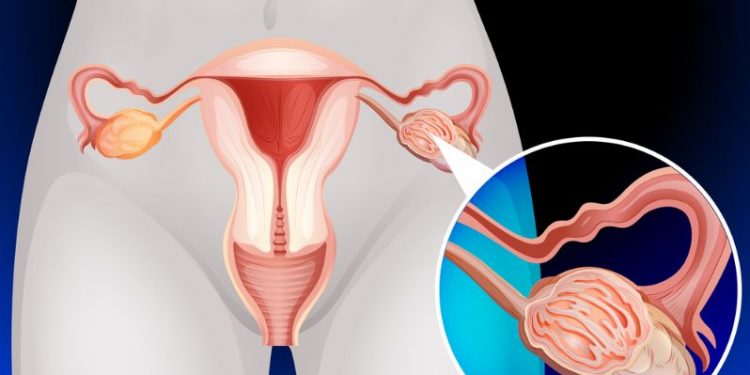
Epithelial ovarian carcinoma (also called primary ovarian carcinoma or epithelial ovary tumor) is the most common type of ovarian cancer. It develops when cells in the lining of the ovaries change their genetic code.
It can start in one or both ovaries, the fallopian tubes, or in the uterus. It can also start in a small area of the ovaries, known as a cyst or nodule.
In most cases, these tumors are very slow-growing and don’t cause symptoms. However, they can be very dangerous if they grow and get large enough to interfere with the normal menstrual cycle or cause health problems such as bleeding.
Your doctor will check for ovarian cancer by looking at your ovaries and other parts of your pelvis, and by taking a sample of fluid from your abdomen. The sample can be sent to a lab for testing.
You’ll probably be referred to a doctor who specializes in treating women with ovarian cancer. This person will decide what treatment is best for you.
Ovarian cancer can be treated with surgery, targeted therapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. These treatments are designed to kill the cancer cells and stop them from growing and spreading.

Surgically staging the cancer helps your doctor figure out what type of treatment is needed. The goal of surgery is to remove as much of the tumor as possible, without removing healthy tissue. Your uterus, both fallopian tubes and both ovaries are removed during this procedure, along with some of the omentum (fatty tissue from the upper abdomen near the stomach and intestines).
After surgery, you might get chemotherapy to shrink the tumors or make them smaller. It’s important to have a good response to the treatment so that it isn’t necessary to have more surgery.
Chemotherapy usually starts after surgery and is usually given for a few months, sometimes more than that. The drugs used most often are carboplatin and paclitaxel. Other medications include cisplatin and docetaxel.
Your doctor may also recommend hormone therapy or immunotherapy if the cancer is in the ovaries or has spread to nearby lymph nodes. These types of treatment can help reduce pain and other symptoms by boosting your immune system.
Some women with ovarian cancer have a buildup of fluid in their abdomen that can cause discomfort and is called ascites. This can be treated with a procedure called paracentesis, in which a needle is inserted into the abdomen and the fluid withdrawn.
People with ovarian cancer that hasn’t spread to the ovaries or other parts of the pelvis have a high survival rate, especially when it is found early. But ovarian cancer that has spread to nearby areas has a poorer outlook.