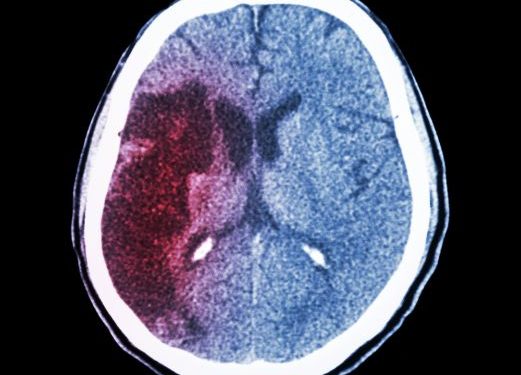
The most common form of astrocytoma in children is low grade, and the primary treatment is surgical resection. However, it is important to note that a child should not undergo surgery unless a tumor is more than half-inch wide. The surgeon should be very careful when removing a childhood astrocytoma, as the tumor may be too large to remove in a surgical procedure.
In a population-based study of astrocytomas in children, the authors removed the bias that may be present in series based on the experience of a particular surgeon or medical center. There were 179 cases of astrocytomas, with an average age of eight years. More than half of the astrocytomas were located in the cerebellum, and the incidence peaked between 1965 and 1970.
Treatment options for astrocytomas in childhood include chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Depending on the location of the tumour, the doctor may prescribe steroids or other drugs to reduce swelling. Generally, a child with a high-grade astrocytoma will undergo surgery. Depending on where the tumour is located, the surgeon can remove as much of the tumor as possible during surgery. Although this can be challenging, surgeons are able to successfully remove as much of the tumour as possible.
If a child develops astrocytoma, the type and stage of the disease will determine the prognosis. While a child’s age will affect the location of the tumor, the type of treatment chosen will determine how far the patient will progress. Several treatments will be necessary to ensure the highest chance of successful treatment. If a patient has a high-grade astrocytoma, it will likely require lifelong care.
The main treatment for astrocytomas in childhood is surgery. A surgeon will attempt to remove as much of the tumour as possible. Sometimes, however, this is not possible. The surgeon might not be able to remove the entire tumour during surgery, and may leave behind some normal brain tissue. If this is the case, treatment options can include chemotherapy or radiotherapy. There are several other treatment options for astrocytomas in childhood.
The location of the astrocytoma may be influenced by the child’s age. The symptoms of the disorder may be related to the child’s age. If you suspect a child has an astrocytoma, you should contact the appropriate medical team. It is important to seek prompt medical care because the condition can affect your child’s health and development. The right treatment can minimize the risk of complications and lead to better quality of life.
The most common treatment for astrocytomas in childhood is surgery. Surgical procedures are effective at removing the tumor and surrounding tissue. However, this may not be possible in all cases. Even if a surgeon is able to remove the tumour, the procedure may leave behind some of the normal brain tissue. In such cases, your child will need to undergo additional surgery to correct the problem. It is important to note that astrocytoma in childhood is a serious medical condition and requires a doctor to properly diagnose it.