The symptoms of fungal infections depend on the type and severity of the infection, and also on a person’s immune system and health. Some symptoms are easy to recognize and treat, while others may be harder to identify.
Fungal infection symptoms can range from a small red, itchy rash (like athlete’s foot or ringworm) to serious health problems like fungal meningitis and pneumonia. People can catch fungal infections from contact with infected animals or contaminated skin and soil.
Your body’s immune system normally protects your skin and mucous membranes from infection by a variety of bacteria, fungi and viruses. However, a number of things can weaken your immune system, including certain conditions (like HIV/AIDS or cancer), medications and smoking.
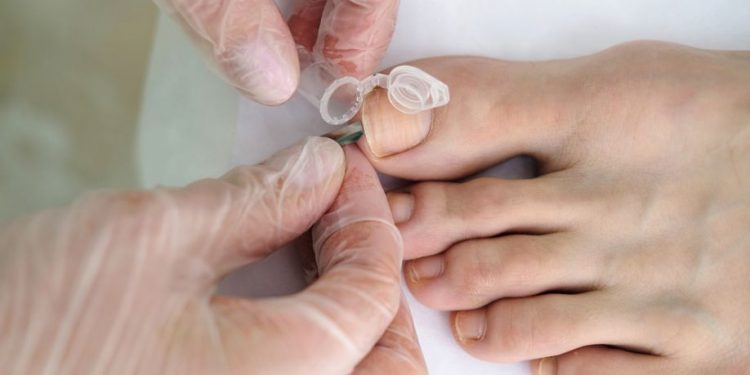
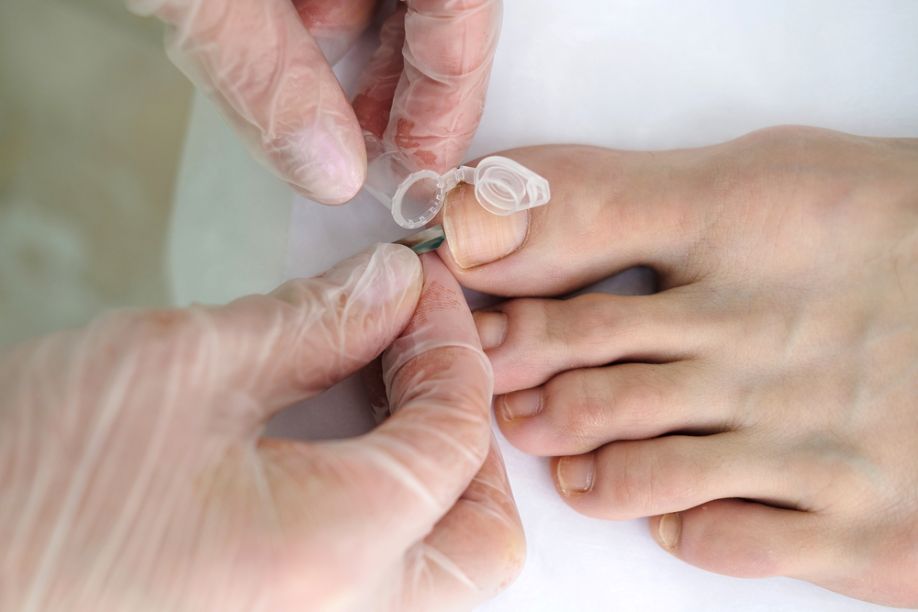
Some fungi that naturally live on your skin, hair and nails can cause a skin infection, called dermatophytosis. This is what causes ringworm, athlete’s foot (tinea pedis), jock itch (tinea cruris) and some other infections of the skin, toes and scalp.
Symptoms of a fungal infection usually start on your skin and look like red, itchy, dry or flaky spots, sometimes with white patches. You may also feel a burning or itching sensation and have a fever. Some fungi are resistant to antifungal medications, so you’ll need to be treated with a doctor.
Fungi can also invade your digestive tract and affect deeper tissues, such as your liver or lungs. This is known as disseminated infection, and it can be very dangerous in immunocompromised people. Some fungi, such as histoplasmosis and pneumocystis jirovecii, can be inhaled and cause lung infections or even pneumonia.
Another common fungal infection is a yeast infection, called candidiasis. Candida is a yeast that naturally lives on your skin and in some other parts of your body, but it can become overactive under certain conditions and cause an infection.
The yeast can spread to other areas of your body, such as the groin (Jock’s itch), the mouth or throat (oral thrush) and the vagina (vulvovaginal candidiasis). Some people have recurrent fungal infections, which can be a sign that their immune system is weakened.
Infections can happen anywhere in your body but are most commonly found on the surface of your skin, in your nails or on your mucous membranes. The fungal infection can be mild, and the itching and redness go away. But it may come back if you don’t get treatment.
You can catch a fungal infection by touching infected skin or hair, or by breathing in spores that have fallen off infected animals or contaminated skin. It can also spread to other people through shared towels, bedding or clothes.
Most superficial infections of the skin and nail (dermatophytes) can be treated with over-the-counter or prescription antifungal medicines, and they will clear up quickly. More severe fungal infections, such as recurrent oral or vaginal thrush, should be treated by your doctor.
Athlete’s foot, ringworm and some other fungal infections are caused by a yeast called Candida. These infections are more common in people who live in damp, humid environments and wear synthetic clothing or sweat a lot.