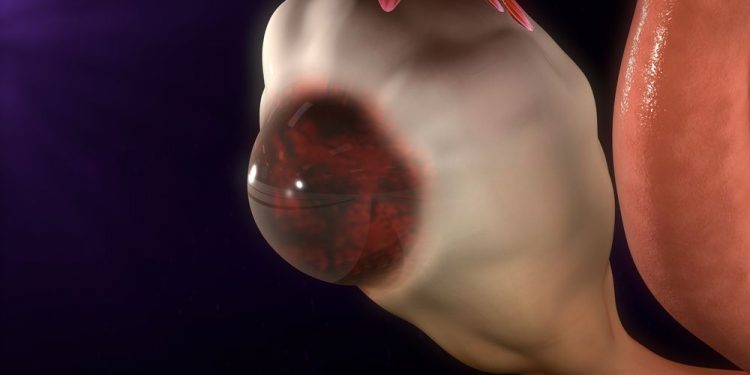
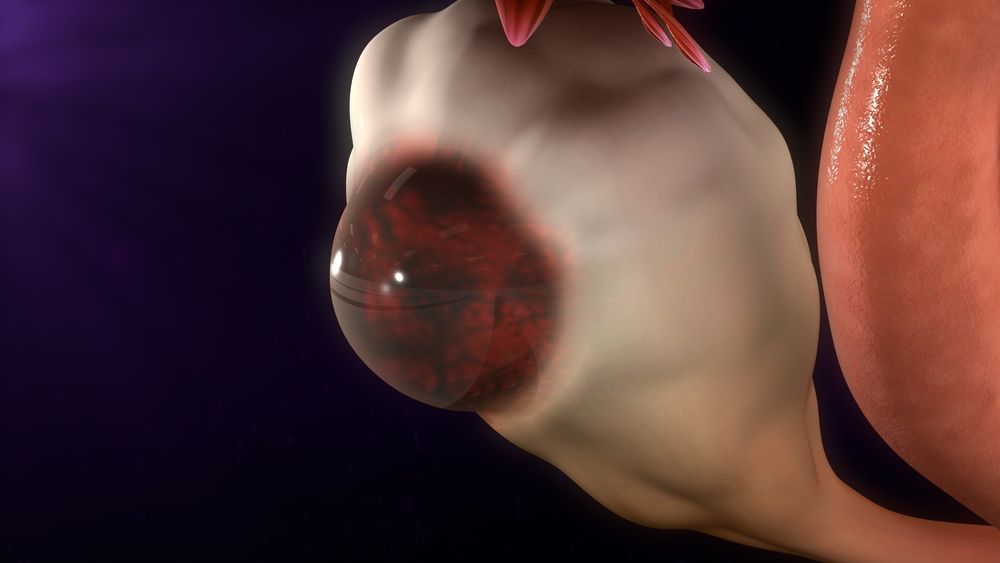
Women’s uterine lining changes in thickness every month during menstruation, in order to host a fertilized egg and support the growing placenta. A healthy lining is essential to conception and pregnancy. However, an overly thick endometrial lining may be a sign of a health issue, such as endometriosis or hyperplasia. The normal thickness of the lining varies from person to person and throughout each phase of life, including childhood, during the reproductive years, and after menopause. It can also be affected by certain health conditions and treatments, such as hormone replacement therapy.
During the proliferative or growth phase, which lasts from days 5 to 14, the endometrial lining becomes enriched with blood to prepare for ovulation and pregnancy. It develops a trilaminar or striated appearance and measures 12-13 mm in thickness. During the secretory phase, which begins after ovulation and lasts until days 15 to 28, the lining thins to less than five millimeters in postmenopausal women who are not on hormone therapy.
The thickest lining during the luteal or secretory phase is important for pregnancy because a fertilized egg implanted into this lining will provide nutrients to the developing placenta and supply the fetus with oxygen, blood, and other vital nutrients. If the lining is too thin, an embryo cannot implant and pregnancy will not be possible.
An overly thick lining can be caused by various issues, including an imbalance of the hormones estrogen and progesterone, endometriosis, fibroids, or other health conditions that affect fertility. This can lead to pelvic pain and heavy bleeding during menstruation. In some cases, it can also prevent a woman from getting pregnant.
Diagnosing an abnormally thick uterine lining is often easy for healthcare providers. Your doctor can perform a transvaginal ultrasound to see the lining of your uterus. Alternatively, they may use a hysteroscopy to see inside your uterus and take a sample for a biopsy. If the lining is too thick, your doctor will prescribe hormones to restore the balance of estrogen and progesterone, which can help improve the chances for pregnancy.
Some lifestyle changes can also increase your chances of a thinner endometrial lining, such as avoiding alcohol and caffeine, which reduce blood flow to the uterus. Regular exercise can also help. The dietary recommendations for women who want to get pregnant include eating foods high in fiber, which promotes regularity and may help thin the lining. Getting enough sleep can also improve the condition of your lining, as well as decreasing stress and anxiety, which can cause the lining to become thinner. Taking vitamin C supplements can also help, as it is an antioxidant that protects cells from damage and can decrease the thickness of the lining. The lining of your uterus is also more likely to be thin if you stop smoking. Smoking can lead to a variety of health problems, including lung cancer. The best way to quit is to speak with your healthcare provider about the options available to you.