Thrombosis symptoms vary from person to person and are often a sign of a more serious problem. If you have any of these symptoms, get to a doctor as soon as possible. You may need an imaging test to look for blood clots in your body.
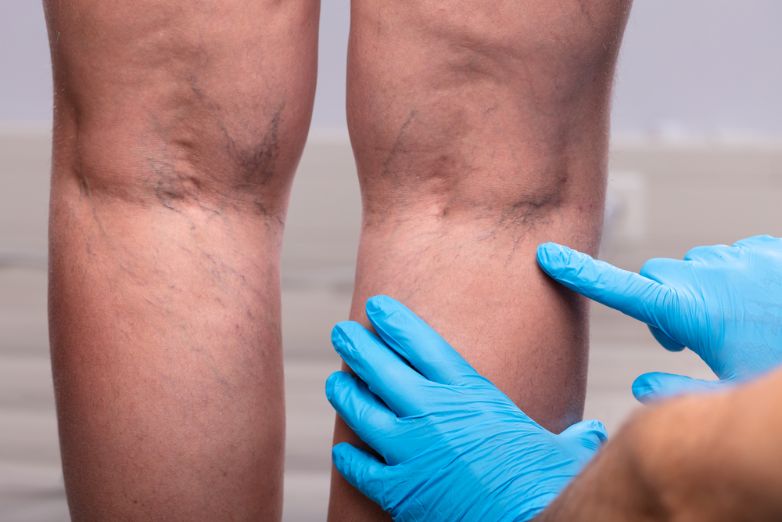
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition where a blood clot forms in a large vein that’s deep in your body. It usually happens in your legs but can also happen in other parts of your body, including your arms and pelvis. The main symptom is pain or swelling in your leg that can’t be relieved by stretching or resting.
People with a DVT are at high risk of a pulmonary embolism (PE). PE happens when a clot from a DVT breaks free and travels to your lungs. It can cause chest pain, shortness of breath and lightheadedness.
The clot from DVT usually stays in your leg, but it can also break free and travel to other parts of your body, like the arm or pelvis. Depending on how severe the clot is, it can be a life-threatening problem that requires treatment.
Other symptoms of DVT can include a persistent, throbbing or cramp-like feeling in your leg that feels painful when you move or stand. This pain doesn’t go away and usually gets worse with time.
Your doctor can tell you if you have a clot in your leg by doing an ultrasound scan. The doctor can see where the clot is located and check for any other problems that might be causing the problem, such as an infection or a damaged vein.
Some doctors also use a dye to make it easier to see your veins and look for clots. This is called venography and can help your doctor diagnose a DVT quickly.
The best way to prevent clots is to avoid smoking or using other tobacco products. If you do smoke or use other forms of tobacco, be sure to quit as soon as possible.
Exercise and eating a healthy diet can also lower your risk of getting a clot. Try to exercise for at least 150 minutes a week and eat a balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables and lean protein.
Your health care provider can also recommend lifestyle changes to help reduce your risk of clots, such as quitting tobacco use and managing your weight. These changes can also help you feel better as you heal.
A clot from your artery may be more serious than one from a vein, and it might cause heart attack or stroke. Your doctor will likely treat it as an emergency and order tests to find out if you have a clot that’s blocking your artery.
If you’ve been diagnosed with a clot that’s blocking an artery, your doctor will probably start with medication to clear the blockage and to increase blood flow to your artery. This can take a few days or weeks, depending on the location and size of your clot.