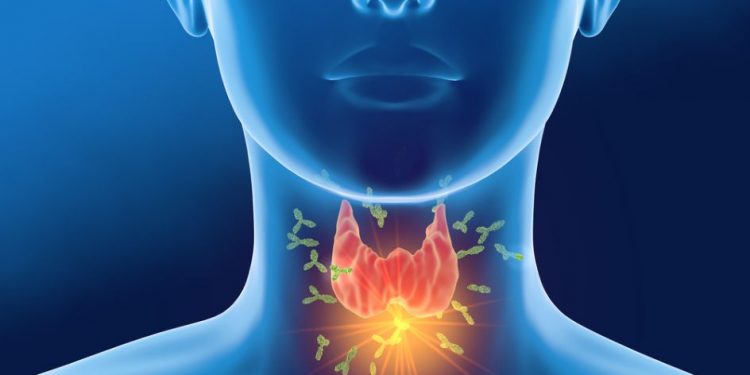
Thyroiditis symptoms depend on the type of thyroiditis and its phase (the time in which the inflammation of the gland results in a change in the level of hormones). In most cases, a clinical examination and blood tests help your doctor diagnose the type and cause of your symptoms.
The most common type of thyroiditis is Hashimoto’s disease, which is an autoimmune (autoimmune means the body attacks itself) illness that affects the thyroid. It can be treated with medicines and often gets better within a few months.
Another type is postpartum thyroiditis, which occurs in women who have recently given birth and which is usually caused by the immune system attacking the gland. It causes a temporary rise in thyroid hormone levels (thyrotoxicosis) and symptoms of an overactive thyroid gland.
A rare type of thyroiditis is called Riedel’s struma or invasive fibrous thyroiditis, which can cause a hard lump to develop in the front of your neck. This is most commonly seen in children, but can happen to adults as well.
Symptoms vary, but may include a hoarse voice, difficulty swallowing or breathing and choking. Other symptoms include swollen lymph nodes and an enlarged thyroid gland.
Thyroiditis can be triggered by a range of things, including infection, medication or an allergy. Inflammation of the thyroid can also occur after surgery, treatment of hyperthyroidism or radiation therapy.

Infections of the ear, sinus or throat can lead to a condition called subacute thyroiditis. This usually occurs a few weeks after a viral infection, such as mumps or flu, but it can also occur at other times. It is more common in middle-aged women than in younger people, but it can affect anyone.
The most common symptom of subacute thyroiditis is pain in the neck, which can radiate to your jaw or ears. If this symptom is severe, your doctor may prescribe steroids or anti-inflammatory medicines. Your thyroid gland usually recovers fully over a few months, but the low level of thyroid hormone (hypothyroidism) may continue.
If your thyroid gland does not recover completely, you will need to take thyroid hormone medicine for a long time. You will have regular blood tests to check your thyroid hormone levels and make sure your thyroid gland is working properly.
Thyroiditis can also be a sign of a serious condition, such as thyroid cancer. If this is the case, it is important to get diagnosed quickly and get appropriate treatment.
Acute infectious thyroiditis is a bacterial infection of the thyroid, most often caused by a piriform sinus fistula that allows bacterial infections to enter the nose, mouth and neck. Acute infectious thyroiditis can cause a range of symptoms, including high temperature, swelling of the thyroid and problems with your heartbeat and blood pressure.
Your symptoms will be worse in the early days, and they will usually settle after antibiotics are taken. However, they can be difficult to treat and can lead to a systemic infection. If this happens, a fine needle aspiration biopsy of the thyroid will be needed to check for other problems.