Tinea capitis is a fungal infection that causes yellow, brown, or white patches on the scalp. The condition can also cause hair loss and baldness, but can be cured with proper treatment.
Tinea capitis can be caused by dermatophytes, which are fungi that grow in warm, moist conditions. Humans and animals can become infected by these fungi. Fungi spread to humans when they come in contact with an infected person, or by touching infected objects. To avoid this, keep your hair and skin clean. Wear clean clothing, wash your hair regularly, and sterilize infected items.
Tinea capitis symptoms include scaly, crusty patches on the scalp and surrounding area. These spots may ooze pus or be filled with red, painful swellings. It can be painful and uncomfortable, and can result in permanent scars if not treated quickly. There are several treatments available, including antifungal shampoos, oral medication, and topical products. If you or your child develops this condition, follow the doctor’s instructions closely to minimize discomfort and speed the healing process.
When someone becomes infected with ringworm, the infection usually starts in the hair. The affected hair will break off above the surface of the scalp. In some cases, pus-filled abscesses will form on the hair shaft.
To prevent tinea capitis from becoming a serious problem, the patient should use medicated shampoos and wear clean clothes. A person with this condition should also be extra cautious when playing in the park or visiting a swimming pool. This can prevent a person from getting a ringworm infection from another person.
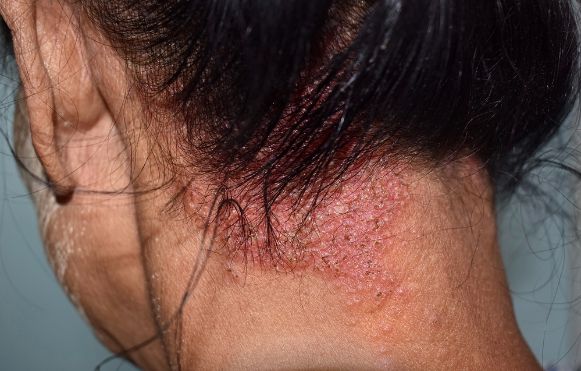
Symptoms of a tinea capitis infection include yellow, white, or brown crusts on the scalp, a scaling appearance, and itching. Some symptoms may not occur until two weeks after a person has contacted the fungi. Children are especially vulnerable to ringworm because they have weakened immune systems.
A tinea capitis infection can be treated with topical agents and oral medications. Topical agents work by killing the fungi. You can use shampoos that contain selenium sulfide, ketoconazole, or tetracycline. Oral medication is usually prescribed for six weeks. Alternatively, a follow-up exam may be needed after four to six weeks. Depending on the results, additional tests may be necessary to rule out other medical disorders.
Ringworm can be transmitted by contact with an infected person or a contaminated object. People can also contract the infection through sharing combs and other grooming tools. Additionally, farm animals can spread ringworm.
Tinea capitis is a very contagious disease that can lead to long-term complications. While it is not a life-threatening condition, it can be uncomfortable, painful, and embarrassing. If you or your child has this infection, be sure to seek medical care immediately. Even when you are treated correctly, a tinea capitis infection can take a long time to heal.
In addition, it can leave you with a lasting ringworm infection. Treating a ringworm infection is a complicated process. You must stay away from infected people, wear clean clothes, and bathe regularly.