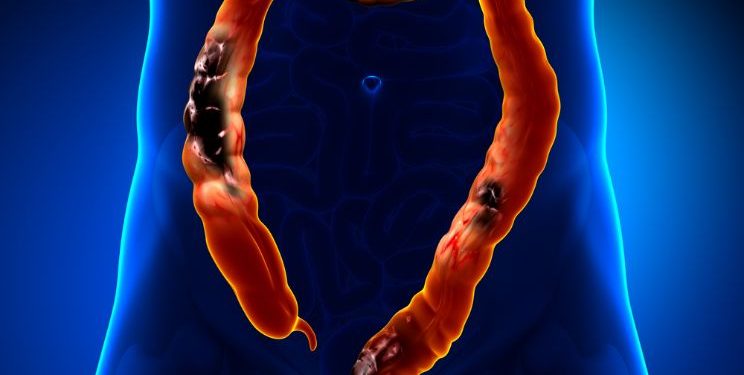
Ulcerative colitis is a form of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). It can affect the rectum, part of the colon and an entire section of the large intestine. It’s a very common symptom and causes diarrhea, abdominal pain and cramping, and bloody stools.
A person with ulcerative colitis might also have other symptoms such as fatigue, weight loss and rectal bleeding. These symptoms can be very debilitating, especially for someone who is not used to them.
Diarrhea is the most obvious symptom of ulcerative colitis, but it may occur at any time. It can happen more often if you’re taking medication or are not eating well.
Other common colitis symptoms are stomach pain, bloating, and constipation. These symptoms are sometimes more severe and longer-lasting than diarrhea.
Getting to the root of your colitis symptoms is an important step in treating it. Your healthcare provider will ask you a lot of questions to make sure there isn’t another health condition that might be causing your symptoms. They will then perform a physical examination and ask you to perform some tests to get a clear diagnosis.
You may have a flexible sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy, which involves inserting a thin, flexible tube into your rectum to look inside your intestine for signs of inflammation and ulcers. You might also have a biopsy to take a small sample of tissue from the affected area for examination by a pathologist.
Your doctor will also give you a full medical history. This will help them find out what your symptoms were before they started, and what your diet is like. They’ll be able to identify the causes of your symptoms and determine which treatment is right for you.
If you have an unusually high white blood cell count, this might be a sign of inflammation in another part of your body. Your doctor can do blood tests, stool samples and other tests to confirm your diagnosis.
Stool tests can be done by drawing a small amount of your poop into a test tube and sending it to the lab. They will check for protein and other markers of inflammation. They can also check for bacteria and other infections.
Your doctor can also do X-rays of your belly to check for narrowed areas, blockages, or other problems. This can be done with a special dye, called barium, which coats the organs and makes them easier to see on X-rays.
Depending on the severity of your symptoms, your doctor might prescribe medication to help control them. This might include antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs such as corticosteroids or 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA). These medicines will fight infection in the lining of your colon and let it heal.
Diet and a change of lifestyle can help alleviate some of the symptoms of colitis. It’s best to try and follow a healthy, balanced diet with lots of fruit, vegetables, and protein, and to avoid foods that cause inflammation. This includes gluten and dairy products, which may make symptoms worse.